Abstract
Objective
As opposed to fundamental investigations into the nature of atrial fibrillation (AF) current clinical studies of AF ablation techniques sometimes only contain sparse information about the underlying electrophysiological properties. The purpose of this prospective, pilot study was to evaluate acute therapeutic success and clinical outcome after 6 month of segmental ostial ablation (SOA) using the High Density Mesh Mapper catheter (HDMM, BARD Electrophysiology, Lowell, MA, USA) for an electrophysiological guided approach. The HDMM is a novel, single expandable basket electrode catheter for high resolution recordings at the left atrium/pulmonary vein (PV) junction.
Methods
SOA was performed by irrigated radiofrequency (RF) application around the HDMM. Entry- and exit conduction block, as well as decreased local electrode amplitude, were endpoints for short-term successful ablation.
Results
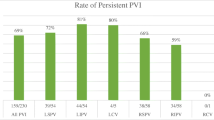
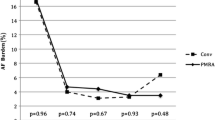
Seventy-two patients with highly symptomatic paroxysmal AF (PAF; 47, 65.2%), persistent AF (12, 16.7%) and permanent AF (13, 18.1%) were studied. Entrance conduction block was obtained in 93%, exit conduction block in 81% of all PV. After 6 month no PV stenosis was observed, 62 patients (86.1%) improved clinically, whereas 52 patients (72.2%) were free from arrhythmias and sinus rhythm was present favoring patients with PAF.
Conclusions
In this first prospective study of PV isolation using the HDMM, our findings suggest, that this method is safe and yields good primary success rates and favourable clinical outcome at 6 month. The new technology based on high resolution recordings, offers beside good anatomical orientation a direct electrophysiological control for monitoring of bidirectional conduction block.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AF:
-
Atrial Fibrillation
- CCL:
-
Continuous Circular Lesions
- HDMM:
-
High Density Mesh Mapper
- LIPV:
-
Left Inferior Pulmonary Vein
- LSPV:
-
Left Superior Pulmonary Vein
- PAF:
-
Paroxysmal AF
- PV:
-
Pulmonary Vein(s)
- RF:
-
Radio Frequency
- RIPV:
-
Right Inferior Pulmonary Vein
- RSPV:
-
Right Superior Pulmonary Vein
- SOA:
-
Segmental Ostial Ablation
References
Haïssaguerre, M., Jaïs, P., Shah, D., Takahashi, A., Hocini, M., Quiniou, G., et al. (1998). Spontaneous initiation of atrial fibrillation by ectopic beats originating in the pulmonary veins. The New England Journal of Medicine, 339, 659–666.
Oral, H., Knight, B. P., Tada, H., Özaydin, M., Chugh, A., Hassan, S., et al. (2002). Pulmonary vein isolation for paroxysmal and persistent atrial fibrillation. Circulation, 105, 1077–1081.
Pappone, C., Oreto, G., Rosanio, S., Vicedomini, G., Tocchi, M., Gugliotta, F., et al. (2001). Atrial electroanatomical remodeling after circumferential radiofrequency pulmonary vein isolation: efficacy of an anatomic approach in a large cohort of patients with atrial fibrillation. Circulation, 104, 2539–2254.
Cox, J. L., Boineau, J. P., Schuessler, R. B., Krater, K. M., & Lappas, D. G. (1993). Five year experience with the Maze procedure for atrial fibrillation. The Annals of Thoracic Surgery, 56, 814–824.
Meissner, A., Christ, M., Maagh, P., Borchard, R., van Bracht, M., Wickenbrock, I., et al. (2007). Quality of life and occurrence of atrial fibrillation in long term follow up of common type atrial flutter: Ablation with irrigated 5 mm tip- and conventional 8 mm tip electrode. Clinical Research in Cardiology; Official Journal of the German Cardiac Society, 96, 794–802.
Haïssaguerre, M., Shah, D., Jaïs, P., Hocini, M., Yamane, T., Deisenhofer, I., et al. (2000). Electrophysiological breakthroughs from the left atrium to the pulmonary veins. Circulation, 102, 2463–2465.
Marrouche, N. F., Dresing, N. F., Cole, C., Bash, D., Saad, E., Balaban, K., et al. (2002). Circular mapping and ablation of the pulmonary veins for treatment of atrial fibrillation: impact of different catheter techniques. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 40, 464–474.
Takahashi, A., Iesaka, Y., Takahashi, Y., Takahashi, R., Kobayashi, K., Takagi, K., et al. (2002). Electrical connections between pulmonary veins: implication for ostial ablation of pulmonary veins in patients with atrial fibrillation. Circulation, 105, 2998–3003.
Oral, H., Scharf, C., Chugh, A., Hall, B., Cheung, P., Good, E., et al. (2003). Catheter ablation for paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. Segmental pulmonary vein ostial ablation versus left atrial ablation. Circulation, 108, 2355–2360.
Karch, M. R., Zrenner, B., Deisenhofer, I., Schreieck, J., Ndrepepa, G., Dong, J., et al. (2005). Freedom of atrial tachyarrhythmias after catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation: A randomized comparison between 2 current ablation strategies. Circulation, 111, 2875–2880.
Ouyang, F., Bänsch, D., Ernst, S., Schaumann, A., Hachiya, H., Chen, M., et al. (2004). Complete Isolation of left atrium surrounding the pulmonary veins. New insights from the double-lasso technique in paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. Circulation, 110, 2090–2096.
Arrudo, M. S., He, D. S., Sheng, D., Friedmann, P., Nakagawa, H., Bruce, C., et al. (2007). A novel mesh electrode catheter for mapping and radiofrequency delivery at the left atrium-pulmonary vein junction: A single-catheter approach to pulmonary vein antrum isolation. Journal of Cardiovascular Electrophysiology, 18, 206–211.
Ott, P., Kirk, M. M., Koo, C., Sheng, D., Bhattacharya, B., & Buxton, A. (2007). Coronary sinus and fossa ovalis ablation: Effect on interatrial conduction and atrial fibrillation. Journal of Cardiovascular Electrophysiology, 18, 1–8.
Ernst, S., Ouyang, F., Löber, F., Antz, M., & Kuck, K. H. (2003). Catheter induced linear lesions in the left atrium in patients with atrial fibrillation. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 42, 1271–1282.
Hocini, M., Sanders, P., Jais, P., Hsu, L. F., Weerasoriya, R., Scavée, C., et al. (2005). Prevalence of pulmonary vein disconnection after anatomical ablation for atrial fibrillation: consequences of wide atrial encircling of the pulmonary veins. European Heart Journal, 26, 696–704.
Nademanee, K., Mc Kenzie, J., Kosar, E., Schwab, M., Sunsaneewitayakul, B., Vasavakul, C., et al. (2004). A new approach for catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation: mapping of the electrophysiological substrate. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 43, 2044–2053.
Chen, S. A., Hsiech, M. H., Tai, C. T., Tsai, C. F., Yu, W. C., Hsu, T. L., et al. (1999). Initiation of atrial fibrillation by ectopic beats originating from the pulmonary veins: electrophysiological characteristics, pharmacological response, and effects of radiofrequency ablation. Circulation, 100, 1879–1886.
Haïssaguerre, M., Jaïs, P., Shah, D. C., Garrigue, S., Takahashi, A., Lavergne, T., et al. (2000). Electrophysiological endpoint for catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation initiated from multiple pulmonary vein foci. Circulation, 101, 1409–1417.
Jaïs, P., Hocini, M., Macale, L., Choi, H. J., Deisenhofer, I., Weerasooriya, R., et al. (2002). Distinctive electrophysiological properties of pulmonary veins in patients with atrial fibrillation. Circulation, 206, 2479–2485.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Meissner, A., van Bracht, M., Schrage, MO. et al. Segmental pulmonary vein isolation in atrial fibrillation: new insights from the high density mesh mapper technique in an electrophysiologically guided approach. J Interv Card Electrophysiol 25, 183–192 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10840-009-9365-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10840-009-9365-z