Abstract
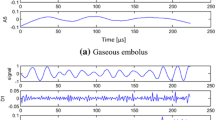
The objective of this study was to develop an analysis method for the automatic detection of intracoronary microemboli triggered high intensity signals (HITS) during percutaneous coronary interventions (PCI). The recorded ultrasonic Doppler velocity spectra from an intracoronary ultrasonic guide-wire were decomposed into 13 wavelet scales applying the continuous wavelet transform. From 7 wavelet scales which were most suitable for a differentiation between HITS and pulsatile flow, envelopes were calculated and combined to improve the HITS-to-background noise ratio. For different intensity thresholds the resulting number of HITS was automatically counted and compared with the number estimated by experienced observers. In a first validation trial HITS were detected within a simplified in vitro model with a sensitivity of 89.2% and a positive predictive value of 87.6%. In a following clinical study 211 HITS from 18 patients during PCI were counted manually by the observers. With the developed wavelet-based method 189 HITS were correctly detected (sensitivity of 89.6%, positive predictive value of 85.5%). The introduced new method automatically detects intracoronary HITS for the first time with a reliable accuracy. This may support further studies evaluating the incidence and consequences of coronary microembolization during coronary interventions.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- FIR:
-
Finite impulse response filter
- fn:
-
False negative
- fp:
-
False positive
- HITS:
-
High intensity signals
- MPC:
-
Medical personal computer
- PCI:
-
Percutaneous coronary intervention
- PPV:
-
Positive predictive value
- SENS:
-
Sensitivity
- tp:
-
True positive
References
Aydin N., Marvasti F., Markus H. S. (2004) Embolic Doppler ultrasound signal detection using discrete wavelet transform. IEEE Trans. Inf. Technol. Biomed. 8(2):182–190
Aydin N., Padayachee S., Markus H. S. (1999) The use of the wavelet transform to describe embolic signals. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 25(6):953–958
Bahrmann P., Figulla H. R., Wagner M., Ferrari M., Voss A., Werner G. S. (2005) Detection of coronary microembolisation by Doppler ultrasound during percutaneous coronary interventions. Heart 91(9):1186–1192
Bahrmann P., Werner G. S., Heusch G., Ferrari M., Poerner T. C., Voss A., Figulla H. R. (2007) Detection of coronary microembolization by Doppler ultrasound in patients with stable angina pectoris undergoing elective percutaneous coronary interventions. Circulation 115(5):600–608
Brucher R., Russell D. (2002) Automatic online embolus detection and artifact rejection with the first multifrequency transcranial Doppler. Stroke 33(8):1969–1974
Carlino M., De Gregorio J., Di Mario C. (1999) Prevention of distal embolization during saphenous vein graft lesion angioplasty. Experience with a new temporary occlusion and aspiration system. Circulation. 99:3221–3223
Consensus Committee of the Ninth International Cerebral Hemodynamic Symposium (1995) Basic identification criteria of Doppler microembolic signals. Stroke 26:1123
Devuyst G., Vesin J. M., Despland P. A., Bogousslavsky J. (2002) The matching pursuit: a new method of characterizing microembolic signals? Ultrasound Med. Biol. 26(6):1051–1056
Dittrich, R., Ritter M. A., Kaps M., Siebler M., Lees K., Larrue V., Nabavi D. G., Ringelstein E. B., Markus H. S., Droste D. W. (2006) The use of embolic signal detection in multicenter trials to evaluate antiplatelet efficacy: signal analysis and quality control mechanisms in the CARESS (Clopidogrel and Aspirin for Reduction of Emboli in Symptomatic carotid Stenosis) trial. Stroke 37(4):1065–1069
Droste D. W., Hagedorn G., Notzold A., Siemens H. J., Sievers H. H., Kaps M. (1997) Bigated transcranial Doppler for the detection of clinically silent circulating emboli in normal persons and patients with prosthetic cardiac valves. Stroke 28(3):588–592
Eicke B. M., Barth V., Kukowski B. (1996) Cardiac microembolism: prevalence and clinical outcome. J. Neurol. Sci. 136:143–147
Fan L., Boni E., Tortoli P., Evans D. H. (2006) Multigate transcranial Doppler ultrasound system with real-time embolic signal identification and archival. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control. 53(10):1853–1861
Fan L., Evans D. H. (1994) A real-time and fine resolution analyser used to estimate the instantaneous energy distribution of Doppler signals. Ultrasound Med Biol. 20(5):445–462
Georgiadis D., Goeke J., Hill M., Konig M., Nabavi D. G., Stogbauer F., Zunker P., Ringelstein E. B. (1996) A novel technique for identification of doppler microembolic signals based on the coincidence method: in vitro and in vivo evaluation. Stroke. 27(4):683–686
Georgiadis, D., Uhlmann F., Lindner A., Zierz S. (2000) Differentiation between true microembolic signals and artefacts using an arbitrary sample volume. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 26(3):493–496
Kemeny V., Droste D. W., Hermes S., Nabavi D. G., Schulte-Altedorneburg G., Siebler M., Ringelstein E. B. (1999) Automatic embolus detection by a neural network. Stroke 30(4):807–810
Mallat S. G. (1989) A theory for multiresolution signal decomposition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 11(7):674–693
Markus H. S. (2000) Monitoring embolism in real time. Circulation 102:826–828
Markus H. S., Brown M. M. (1993) Differentiation between different pathological cerebral embolic materials using transcranial Doppler in an in vitro model. Stroke. 24(1):1–5
Markus H. S., Loh A., Brown M. M. (1993) Computerized detection of cerebral emboli and discrimination from artifact using Doppler ultrasound. Stroke. 24(11):1667–1672
Markus H. S., Tegeler C. H. (1995) Experimental aspects of high-intensity transient signals in the detection of emboli. J. Clin. Ultrasound 23(2):81–87
Moehring M. A., Spencer M. P. (2002) Power M-mode Doppler (PMD) for observing cerebral blood flow and tracking emboli. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 28(1):49–57
Okamura A., Ito H., Iwakura K., Kawano S., Inoue K., Maekawa Y., Ogihara T., Fujii K. (2005) Detection of embolic particles with the Doppler guide wire during coronary intervention in patients with acute myocardial infarction: efficacy of distal protection device. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 45(2):212–215
Okamura A., Ito H., Iwakura K., Kawano S., Kurotobi T., Date M., Inoue K., Ogihara T., Fujii K. (2007) Detection and quantification of embolic particles during percutaneous coronary intervention to stable plaque: It correlates to coronary flow dynamics and myocardial damage. Catheter. Cardiovasc. Interv. 69(3):425–431
Russell D., Madden K. P., Clark W. M. (1991) Detection of arterial emboli using Doppler ultrasound in rabbits. Stroke 22:253–258
Russell, D., Madden K. P., Clark W. M., Sandset P. M., Zivin J. A. (1991) Detection of arterial emboli using Doppler ultrasound in rabbits. Stroke 22(2):253–258
Saber R. S., Edwards W. D., Bailey K. R. (1993) Coronary embolization after balloon angioplasty or thrombolytic therapy: an autopsy study of 32 cases. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 22:1283–1288
Siebler M., Rose G., Sitzer M., Bender A., Steinmetz H. (1994) Real-time identification of cerebral microemboli with US feature detection by a neural network. Radiology 192(3):739–742
Spencer M. P., Moehring M. A., Jesurum J. (2004) Gram-mode transcranial Doppler for diagnosis of patent foramen ovale and assessing transcatheter closure. J. Neuroimaging 14(4):342–349
Topol E. J., Yadav J. S. (2000) Recognition of the importance of embolization in atherosclerotic vascular disease. Circulation 101:570–580
World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki (2002) Ethical principles for medical research involving human subjects. Nurs. Ethics 9(1):105–109
Zhang Y., Zhang H., Zhang N. (2005) Microembolic signal characterization using adaptive chirplet expansion. IEEE Trans. Ultrason Ferroelectr. Freq. Control. 52(8):1291–1299
Acknowledgments
This study was partly supported by a grant from the Thuringian Ministry of Culture TKM (HWP) and the University of Applied Sciences Jena.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Voss, A., Bahrmann, P., Schröder, R. et al. Automatic Detection of Microemboli During Percutaneous Coronary Interventions. Ann Biomed Eng 35, 2087–2094 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-007-9386-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-007-9386-7