Abstract
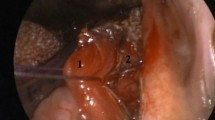
In a patient with unilateral pharyngeal paralysis, rotation of the head to the paralyzed side can effectively close the hemipharynx on that side. However, the exact level or place of closure is unknown. Serial computed tomography of the pharynx in a patient with lateral medullary syndrome showed that hemipharyngeal closing occurred at the level of the hyoid bone, or the hypopharyngeal cavity above the pyriform sinus, and that the entire space of the bilateral pyriform sinuses remained open despite the head rotation.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tsukamoto, Y. CT Study of Closure of the Hemipharynx with Head Rotation in a Case of Lateral Medullary Syndrome. Dysphagia 15, 17–18 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004559910005
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004559910005