Abstract
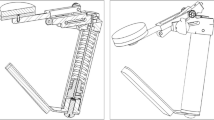
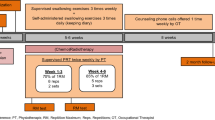
Head and neck cancer (HNC) patients may develop dysphagia due to muscle atrophy and fibrosis following chemoradiotherapy. Strengthening of the swallowing muscles through therapeutic exercise is potentially effective for improving swallowing function. We hypothesize that a customized Swallow Exercise Aid (SEA), developed for isometric and isokinetic strengthening exercises (against resistance), can help to functionally strengthen the suprahyoid musculature, which in turn can improve swallowing function. An effectiveness/feasibility study was carried out with ten senior healthy volunteers, who performed exercises 3 times per day for 6 weeks. Exercises included chin tuck against resistance (CTAR), jaw opening against resistance (JOAR), and effortful swallow exercises with the SEA. Multidimensional assessment consisted of measurements of maximum chin tuck and jaw opening strength, maximum tongue strength/endurance, suprahyoid muscle volume, hyoid bone displacement, swallowing transport times, occurrence of laryngeal penetration/aspiration and/or contrast residue, maximum mouth opening, feasibility/compliance (questionnaires), and subjective swallowing complaints (SWAL-QOL). After 6-weeks exercise, mean chin tuck strength, jaw opening strength, anterior tongue strength, suprahyoid muscle volume, and maximum mouth opening significantly increased (p < .05). Feasibility and compliance (median 86 %, range 48–100 %) of the SEA exercises were good. This prospective effectiveness/feasibility study on the effects of CTAR/JOAR isometric and isokinetic strengthening exercises on swallowing musculature and function shows that senior healthy subjects are able to significantly increase swallowing muscle strength and volume after a 6-week training period. These positive results warrant further investigation of effectiveness and feasibility of these SEA exercises in HNC patients with dysphagia.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Logemann JA. Evaluation and treatment of swallowing disorders. 2nd ed. Austin: Pro-ed; 1998.
Perlman AL, Schulze-Delrieu KS. Deglutition and its disorders. San Diego: Singular Publishing; 1997.
Pearson WG Jr, Hindson DF, Langmore SE, Zumwalt AC. Evaluating swallowing muscles essential for hyolaryngeal elevation by using muscle functional magnetic resonance imaging. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2013;85(3):735–40.
Lazarus CL, Logemann JA, Pauloski BR, Colangelo LA, Kahrilas PJ, Mittal BB, Pierce M. Swallowing disorders in head and neck cancer patients treated with radiotherapy and adjuvant chemotherapy. Laryngoscope. 1996;106(9 Pt 1):1157–66.
Smith RV, Kotz T, Beitler JJ, Wadler S. Long-term swallowing problems after organ preservation therapy with concomitant radiation therapy and intravenous hydroxyurea: initial results. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2000;126(3):384–9.
Nguyen NP, Moltz CC, Frank C, Vos P, Smith HJ, Karlsson U, Dutta S, Midyett FA, Barloon J, Sallah S. Dysphagia following chemoradiation for locally advanced head and neck cancer. Ann Oncol. 2004;15(3):383–8.
Agarwal J, Palwe V, Dutta D, Gupta T, Laskar SG, Budrukkar A, Murthy V, Chaturvedi P, Pai P, Chaukar D, D’Cruz AK, Kulkarni S, Kulkarni A, Baccher G, Shrivastava SK. Objective assessment of swallowing function after definitive concurrent (chemo)radiotherapy in patients with head and neck cancer. Dysphagia. 2011;26(4):399–406.
Lazarus CL, Logemann JA, Pauloski BR, Rademaker AW, Larson CR, Mittal BB, Pierce M. Swallowing and tongue function following treatment for oral and oropharyngeal cancer. J Speech Lang Hear Res. 2000;43(4):1011–23.
Robbins J, Kays SA, Gangnon RE, Hind JA, Hewitt AL, Gentry LR, Taylor AJ. The effects of lingual exercise in stroke patients with dysphagia. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2007;88(2):150–8.
Clark HM, Henson PA, Barber WD, Stierwalt JA, Sherrill M. Relationships among subjective and objective measures of tongue strength and oral phase swallowing impairments. Am J Speech Lang Pathol. 2003;12(1):40–50.
Lazarus C. Tongue strength and exercise in healthy individuals and in head and neck cancer patients. Semin Speech Lang. 2006;27(4):260–7.
Chen AM, Li BQ, Lau DH, Farwell DG, Luu Q, Stuart K, Newman K, Purdy JA, Vijayakumar S. Evaluating the role of prophylactic gastrostomy tube placement prior to definitive chemoradiotherapy for head and neck cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2010;78(4):1026–32.
Kulbersh BD, Rosenthal EL, McGrew BM, Duncan RD, McColloch NL, Carroll WR, Magnuson JS. Pretreatment, preoperative swallowing exercises may improve dysphagia quality of life. Laryngoscope. 2006;116(6):883–6.
Carroll WR, Locher JL, Canon CL, Bohannon IA, McColloch NL, Magnuson JS. Pretreatment swallowing exercises improve swallow function after chemoradiation. Laryngoscope. 2008;118(1):39–43.
van der Molen L, van Rossum MA, Burkhead LM, Smeele LE, Rasch CR, Hilgers FJ. A randomized preventive rehabilitation trial in advanced head and neck cancer patients treated with chemoradiotherapy: feasibility, compliance, and short-term effects. Dysphagia. 2011;26(2):155–70.
Carnaby-Mann G, Crary MA, Schmalfuss I, Amdur R. “Pharyngocise”: randomized controlled trial of preventative exercises to maintain muscle structure and swallowing function during head-and-neck chemoradiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2012;83(1):210–9.
van der Molen L, van Rossum MA, Rasch CR, Smeele LE, Hilgers FJ. Two-year results of a prospective preventive swallowing rehabilitation trial in patients treated with chemoradiation for advanced head and neck cancer. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2014;271(5):1257–70.
Logemann JA, Pauloski BR, Rademaker AW, Colangelo LA. Super-supraglottic swallow in irradiated head and neck cancer patients. Head Neck. 1997;19(6):535–40.
Lazarus C, Logemann JA, Gibbons P. Effects of maneuvers on swallowing function in a dysphagic oral cancer patient. Head Neck. 1993;15(5):419–24.
Hind JA, Nicosia MA, Roecker EB, Carnes ML, Robbins J. Comparison of effortful and noneffortful swallows in healthy middle-aged and older adults. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2001;82(12):1661–5.
Lazarus C, Logemann JA, Song CW, Rademaker AW, Kahrilas PJ. Effects of voluntary maneuvers on tongue base function for swallowing. Folia Phoniatr Logop. 2002;54(4):171–6.
Kahrilas PJ, Logemann JA, Krugler C, Flanagan E. Volitional augmentation of upper esophageal sphincter opening during swallowing. Am J Physiol. 1991;260(3 Pt 1):G450–6.
Shaker R, Kern M, Bardan E, Taylor A, Stewart ET, Hoffmann RG, Arndorfer RC, Hofmann C, Bonnevier J. Augmentation of deglutitive upper esophageal sphincter opening in the elderly by exercise. Am J Physiol. 1997;272(6 Pt 1):G1518–22.
Shaker R, Easterling C, Kern M, Nitschke T, Massey B, Daniels S, Grande B, Kazandjian M, Dikeman K. Rehabilitation of swallowing by exercise in tube-fed patients with pharyngeal dysphagia secondary to abnormal UES opening. Gastroenterology. 2002;122(5):1314–21.
Logemann JA, Rademaker A, Pauloski BR, Kelly A, Stangl-McBreen C, Antinoja J, Grande B, Farquharson J, Kern M, Easterling C, Shaker R. A randomized study comparing the Shaker exercise with traditional therapy: a preliminary study. Dysphagia. 2009;24(4):403–11.
Easterling C, Grande B, Kern M, Sears K, Shaker R. Attaining and maintaining isometric and isokinetic goals of the Shaker exercise. Dysphagia. 2005;20(2):133–8.
Yoon WL, Khoo JK, Rickard Liow SJ. Chin tuck against resistance (CTAR): new method for enhancing suprahyoid muscle activity using a Shaker-type exercise. Dysphagia. 2014;29(2):243–8.
Buchbinder D, Currivan RB, Kaplan AJ, Urken ML. Mobilization regimens for the prevention of jaw hypomobility in the radiated patient: a comparison of three techniques. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1993;51(8):863–7.
Kraaijenga S, van der Molen L, van Tinteren H, Hilgers F, Smeele L. Treatment of myogenic temporomandibular disorder: a prospective randomized clinical trial, comparing a mechanical stretching device (TheraBite) with standard physical therapy exercise. Cranio. 2014;32(3):208–16.
Rinkel RN, Verdonck-de Leeuw IM, Langendijk JA, van Reij EJ, Aaronson NK, Leemans CR. The psychometric and clinical validity of the SWAL-QOL questionnaire in evaluating swallowing problems experienced by patients with oral and oropharyngeal cancer. Oral Oncol. 2009;45(8):e67–71.
Mehanna H, Paleri V, West CM, Nutting C. Head and neck cancer—Part 1: epidemiology, presentation, and prevention. BMJ. 2010;341:c4684.
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61(2):69–90.
Burkhead LM, Sapienza CM, Rosenbek JC. Strength-training exercise in dysphagia rehabilitation: principles, procedures, and directions for future research. Dysphagia. 2007;22(3):251–65.
Wada S, Tohara H, Iida T, Inoue M, Sato M, Ueda K. Jaw-opening exercise for insufficient opening of upper esophageal sphincter. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2012;93(11):1995–9.
Adams V, Mathisen B, Baines S, Lazarus C, Callister R. A systematic review and meta-analysis of measurements of tongue and hand strength and endurance using the Iowa Oral Performance Instrument (IOPI). Dysphagia. 2013;28(3):350–69.
Hewitt A, Hind J, Kays S, Nicosia M, Doyle J, Tompkins W, Gangnon R, Robbins J. Standardized instrument for lingual pressure measurement. Dysphagia. 2008;23(1):16–25.
Leonard RJ, Kendall KA. Dysphagia assessment and treatment planning: a team approach. San Diego: Singular Pub. Group; 1997.
Leonard RJ, Kendall KA, McKenzie S, Goncalves MI, Walker A. Structural displacements in normal swallowing: a videofluoroscopic study. Dysphagia. 2000;15(3):146–52.
Kendall KA, McKenzie S, Leonard RJ, Goncalves MI, Walker A. Timing of events in normal swallowing: a videofluoroscopic study. Dysphagia. 2000;15(2):74–83.
Rosenbek JC, Robbins JA, Roecker EB, Coyle JL, Wood JL. A penetration-aspiration scale. Dysphagia. 1996;11(2):93–8.
Lemmens J, Bours GJ, Limburg M, Beurskens AJ. The feasibility and test-retest reliability of the Dutch Swal-Qol adapted interview version for dysphagic patients with communicative and/or cognitive problems. Qual Life Res. 2013;22(4):891–5.
Crary MA, Carnaby Mann GD, Groher ME. Biomechanical correlates of surface electromyography signals obtained during swallowing by healthy adults. J Speech Lang Hear Res. 2006;49(1):186–93.
Palmer PM, Luschei ES, Jaffe D, McCulloch TM. Contributions of individual muscles to the submental surface electromyogram during swallowing. J Speech Lang Hear Res. 1999;42(6):1378–91.
Acknowledgments
Wim Kraan, emeritus-technician at the Netherlands Cancer Institute, is greatly acknowledged for the technical construction of the Swallow Exercise Aid (SEA). Jan-Ove Persson (Atos Medical, Hörby, Sweden) and Corina J van As-Brooks (PhD, SLP, MBA; Atos Medical and Netherlands Cancer Institute) are acknowledged for their input in the development of the SEA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kraaijenga, S.A.C., van der Molen, L., Stuiver, M.M. et al. Effects of Strengthening Exercises on Swallowing Musculature and Function in Senior Healthy Subjects: a Prospective Effectiveness and Feasibility Study. Dysphagia 30, 392–403 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-015-9611-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-015-9611-8