Abstract
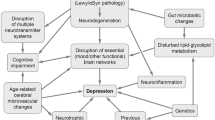
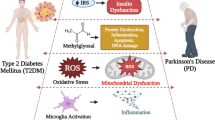
There is ample evidence that impairments in the hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal (HPA) axis are of etiopathobiochemical importance in a subgroup of patients with “depression”, causing hypercortisolaemia as major metabolic effect. Chronic hypercortisolaemia causes insulin resistance. Therefore, it is not surprising that epidemiological studies demonstrate an association of “depression” with diabetes type II and vice versa. Chronic stress and hypercortisolaemia are conditions, which have been suggested to be causal for Alzheimer’s disease (AD) as brain insulin resistance is associated with β-Amyloid-accumulation and hyperphosphorylation of tau-protein. Depression is one of the significant symptomatology preceding AD. It is however, not known whether “depression” associated with hypercortisolaemia is the subgroup at risk for AD. In contrast to a subgroup of “depression” and to AD, in Parkinson’s disease (PD) there is only weak evidence for an association with diabetes type II and insulin resistance. As “depression” is preceding PD in up to half of such patients, it remains to be elucidated whether this is a subgroup of depressed patients, which is not associated with disturbances of the HPA axis and hypercortisolaemia. Improved clinical and biochemical/molecular knowledge about “depression” associated with AD and PD in comparison to “pure” depression might lead to improved therapeutic strategies and even drug development focusing subtypes of “depression”.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexander A (2008) Diabetes and depression–is there a link to the HPA axis? Occup Med (Lond) 58:308 author reply 308
Anisman H (2009) Cascading effects of stressors and inflammatory immune system activation: implications for major depressive disorder. J Psychiatry Neurosci 34:4–20
Arduino DM, Esteves AR, Cardoso SM, Oliveira CR (2009) Endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondria interplay mediates apoptotic cell death: relevance to Parkinson’s disease. Neurochem Int 55:341–348
Area-Gomez E, de Groof AJ, Boldogh I et al (2009) Presenilins are enriched in endoplasmic reticulum membranes associated with mitochondria. Am J Pathol 175:1810–1816
Arvanitakis Z, Wilson RS, Schneider JA, Bienias JL, Evans DA, Bennett DA (2004) Diabetes mellitus and progression of rigidity and gait disturbance in older persons. Neurology 63:996–1001
Arvanitakis Z, Wilson RS, Bienias JL, Bennett DA (2007) Diabetes and parkinsonian signs in older persons. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord 21:144–149
Awad N, Gagnon M, Messier C (2004) The relationship between impaired glucose tolerance, type 2 diabetes, and cognitive function. J Clin Exp Neuropsychol 26:1044–1080
Babri S, Badie HG, Khamenei S, Seyedlar MO (2007) Intrahippocampal insulin improves memory in a passive-avoidance task in male wistar rats. Brain Cogn 64:86–91
Bancher C, Braak H, Fischer P, Jellinger KA (1993) Neuropathological staging of Alzheimer lesions and intellectual status in Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease patients. Neurosci Lett 162:179–182
Becker C, Brobert GP, Johansson S, Jick SS, Meier CR (2008) Diabetes in patients with idiopathic Parkinson’s disease. Diabetes Care 31:1808–1812
Berg D (2008) Biomarkers for the early detection of Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s disease. Neurodegener Dis 5:133–136
Blum-Degen D, Frölich L, Hoyer S, Riederer P (1995) Altered regulation of brain glucose metabolism as a cause of neurodegenerative disorders? J Neural Transm Suppl 46:139–147
Bodis-Wollner I (2003) Neuropsychological and perceptual defects in Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 9(Suppl 2):S83–S89
Braak H, Braak E, Yilmazer D, Schultz C, de Vos RA, Jansen EN (1995) Nigral and extranigral pathology in Parkinson’s disease. J Neural Transm Suppl 46:15–31
Brands AM, Biessels GJ, Kappelle LJ et al (2007) Cognitive functioning and brain MRI in patients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus: a comparative study. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 23:343–350
Brands AM, Kessels RP, Ryan CM (2009) Cognition in adults with type 1 diabetes. In: Biessels GJ, Luchsinger JA (eds) Diabetes and the brain. Humana Press, New York, NY, pp 277–293
Breidert T, Callebert J, Heneka MT, Landreth G, Launay JM, Hirsch EC (2002) Protective action of the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma agonist pioglitazone in a mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. J Neurochem 82:615–624
Brodbeck J, Balestra ME, Saunders AM, Roses AD, Mahley RW, Huang Y (2008) Rosiglitazone increases dendritic spine density and rescues spine loss caused by apolipoprotein E4 in primary cortical neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:1343–1346
Brookmeyer R, Gray S, Kawas C (1998) Projections of Alzheimer’s disease in the United States and the public health impact of delaying disease onset. Am J Public Health 88:1337–1342
Brummett BH, Boyle SH, Siegler IC et al (2008) Effects of environmental stress and gender on associations among symptoms of depression and the serotonin transporter gene linked polymorphic region (5-HTTLPR). Behav Genet 38:34–43
Carnemolla A, Fossale E, Agostoni E et al (2009) Rrs1 is involved in endoplasmic reticulum stress response in Huntington disease. J Biol Chem 284:18167–18173
Charlett A, Dobbs RJ, Purkiss AG et al (1998) Cortisol is higher in parkinsonism and associated with gait deficit. Acta Neurol Scand 97:77–85
Chaturvedi RK, Beal MF (2008) PPAR: a therapeutic target in Parkinson’s disease. J Neurochem 106:506–518
Checkley S (1996) The neuroendocrinology of depression and chronic stress. Br Med Bull 52:597–617
Chevet E, Cameron PH, Pelletier MF, Thomas DY, Bergeron JJ (2001) The endoplasmic reticulum: integration of protein folding, quality control, signaling and degradation. Curr Opin Struct Biol 11:120–124
Clarke DM, Currie KC (2009) Depression, anxiety and their relationship with chronic diseases: a review of the epidemiology, risk and treatment evidence. Med J Aust 190:S54–S60
Coll T, Rodriguez-Calvo R, Barroso E et al (2009) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) beta/delta: a new potential therapeutic target for the treatment of metabolic syndrome. Curr Mol Pharmacol 2:46–55
Cosgrove MP, Sargeant LA, Griffin SJ (2008) Does depression increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes? Occup Med (Lond) 58:7–14
Craft S (2005) Insulin resistance and cognitive impairment: a view through the prism of epidemiology. Arch Neurol 62:1043–1044
Craft S, Newcomer J, Kanne S et al (1996) Memory improvement following induced hyperinsulinemia in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 17:123–130
Craft S, Asthana S, Newcomer JW et al (1999) Enhancement of memory in Alzheimer disease with insulin and somatostatin, but not glucose. Arch Gen Psychiatry 56:1135–1140
Craft S, Asthana S, Cook DG et al (2003) Insulin dose-response effects on memory and plasma amyloid precursor protein in Alzheimer’s disease: interactions with apolipoprotein E genotype. Psychoneuroendocrinology 28:809–822
D’Amelio M, Ragonese P, Callari G et al (2009) Diabetes preceding Parkinson’s disease onset. A case-control study. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 15:660–664
de la Monte SM, Tong M (2009) Mechanisms of nitrosamine-mediated neurodegeneration: potential relevance to sporadic Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis 17(4):817–825
de la Monte SM, Wands JR (2008) Alzheimer’s disease is type 3 diabetes-evidence reviewed. J Diabetes Sci Technol 2:1101–1113
Dehmer T, Heneka MT, Sastre M, Dichgans J, Schulz JB (2004) Protection by pioglitazone in the MPTP model of Parkinson’s disease correlates with I kappa B alpha induction and block of NF kappa B and iNOS activation. J Neurochem 88:494–501
Dhamoon MS, Noble JM, Craft S (2009) Intranasal insulin improves cognition and modulates beta-amyloid in early AD. Neurology 72:292–293 author reply 293–294
Dinan TG (2005) Stress: the shared common component in major mental illnesses. Eur Psychiatry 20(Suppl 3):S326–S328
Djupesland PG (2008) Intranasal insulin improves cognition and modulates beta-amyloid in early AD. Neurology 71:864 author reply 864
Driver JA, Smith A, Buring JE, Gaziano JM, Kurth T, Logroscino G (2008) Prospective cohort study of type 2 diabetes and the risk of Parkinson’s disease. Diabetes Care 31:2003–2005
Duennwald ML, Lindquist S (2008) Impaired ERAD and ER stress are early and specific events in polyglutamine toxicity. Genes Dev 22:3308–3319
El Messari S, Leloup C, Quignon M, Brisorgueil MJ, Penicaud L, Arluison M (1998) Immunocytochemical localization of the insulin-responsive glucose transporter 4 (Glut4) in the rat central nervous system. J Comp Neurol 399:492–512
Elias PK, Elias MF, D’Agostino RB et al (1997) NIDDM and blood pressure as risk factors for poor cognitive performance. The Framingham Study. Diabetes Care 20:1388–1395
Elias MF, Elias PK, Sullivan LM, Wolf PA, D’Agostino RB (2003) Lower cognitive function in the presence of obesity and hypertension: the Framingham heart study. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 27:260–268
Elmquist JK, Marcus JN (2003) Rethinking the central causes of diabetes. Nat Med 9:645–647
Frölich L, Blum-Degen D, Bernstein HG et al (1998) Brain insulin and insulin receptors in aging and sporadic Alzheimer’s disease. J Neural Transm 105:423–438
Frölich L, Blum-Degen D, Riederer P, Hoyer S (1999) A disturbance in the neuronal insulin receptor signal transduction in sporadic Alzheimer’s disease. Ann NY Acad Sci 893:290–293
Fukuyama H, Ogawa M, Yamauchi H et al (1994) Altered cerebral energy metabolism in Alzheimer’s disease: a PET study. J Nucl Med 35:1–6
Ganda OP, Rossini AA, Like AA (1976) Studies on streptozotocin diabetes. Diabetes 25:595–603
Gasparini L, Gouras GK, Wang R et al (2001) Stimulation of beta-amyloid precursor protein trafficking by insulin reduces intraneuronal beta-amyloid and requires mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling. J Neurosci 21:2561–2570
Gerlach M, Reichmann H, Riederer P (eds) (2007) Die Parkinson-Krankheit, 4th edn. Springer, Wien-New York, Wien
Golden SH (2007) A review of the evidence for a neuroendocrine link between stress, depression and diabetes mellitus. Curr Diabetes Rev 3:252–259
Grosskreutz J, Van Den Bosch L, Keller BU (2010) Calcium dysregulation in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Cell Calcium 47(2):165–174
Grünblatt E (2008) Commonalities in the genetics of Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease. Expert Rev Neurother 8:1865–1877
Grünblatt E, Hoyer S, Riederer P (2004) Gene expression profile in streptozotocin rat model for sporadic Alzheimer’s disease. J Neural Transm 111:367–386
Grünblatt E, Koutsilieri E, Hoyer S, Riederer P (2006) Gene expression alterations in brain areas of intracerebroventricular streptozotocin treated rat. J Alzheimers Dis 9:261–271
Grünblatt E, Salkovic-Petrisic M, Osmanovic J, Riederer P, Hoyer S (2007) Brain insulin system dysfunction in streptozotocin intracerebroventricularly treated rats generates hyperphosphorylated tau protein. J Neurochem 101:757–770
Grünblatt E, Zehetmayer S, Bartl J et al (2009) Genetic risk factors and markers for Alzheimer’s disease and/or depression in the VITA study. J Psychiatr Res 43(3):298–308
Haense C, Herholz K, Jagust WJ, Heiss WD (2009) Performance of FDG PET for detection of Alzheimer’s disease in two independent multicentre samples (NEST-DD and ADNI). Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 28:259–266
Hassing LB, Grant MD, Hofer SM et al (2004a) Type 2 diabetes mellitus contributes to cognitive decline in old age: a longitudinal population-based study. J Int Neuropsychol Soc 10:599–607
Hassing LB, Hofer SM, Nilsson SE et al (2004b) Comorbid type 2 diabetes mellitus and hypertension exacerbates cognitive decline: evidence from a longitudinal study. Age Ageing 33:355–361
Hassing LB, Dahl AK, Thorvaldsson V et al (2009) Overweight in midlife and risk of dementia: a 40-year follow-up study. Int J Obes (Lond) 33:893–898
Herholz K (2003) PET studies in dementia. Ann Nucl Med 17:79–89
Hirsch EC, Hunot S (2009) Neuroinflammation in Parkinson’s disease: a target for neuroprotection? Lancet Neurol 8:382–397
Hoyer S (1997) Models of Alzheimer’s disease: cellular and molecular aspects. J Neural Transm Suppl 49:11–21
Hoyer S (1998) Is sporadic Alzheimer disease the brain type of non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus? A challenging hypothesis. J Neural Transm 105:415–422
Hoyer S (2004) Glucose metabolism and insulin receptor signal transduction in Alzheimer disease. Eur J Pharmacol 490:115–125
Hoyer S, Lannert H (1999) Inhibition of the neuronal insulin receptor causes Alzheimer-like disturbances in oxidative/energy brain metabolism and in behavior in adult rats. Ann NY Acad Sci 893:301–303
Hoyer S, Muller D, Plaschke K (1994) Desensitization of brain insulin receptor. Effect on glucose/energy and related metabolism. J Neural Transm Suppl 44:259–268
Hoyer S, Lannert H, Noldner M, Chatterjee SS (1999) Damaged neuronal energy metabolism and behavior are improved by Ginkgo biloba extract (EGb 761). J Neural Transm 106:1171–1188
Hoyer S, Lee SK, Loffler T, Schliebs R (2000) Inhibition of the neuronal insulin receptor. An in vivo model for sporadic Alzheimer disease? Ann NY Acad Sci 920:256–258
Hu G, Jousilahti P, Bidel S, Antikainen R, Tuomilehto J (2007) Type 2 diabetes and the risk of Parkinson’s disease. Diabetes Care 30:842–847
Huang HJ, Liang KC, Chang YY, Ke HC, Lin JY, Hsieh-Li HM (2009) The interaction between acute oligomer Abeta(1–40) and stress severely impaired spatial learning and memory. Neurobiol Learn Mem 93:8–18
Hunter RL, Dragicevic N, Seifert K et al (2007) Inflammation induces mitochondrial dysfunction and dopaminergic neurodegeneration in the nigrostriatal system. J Neurochem 100:1375–1386
Ikesugi K, Mulhern ML, Madson CJ et al (2006) Induction of endoplasmic reticulum stress in retinal pericytes by glucose deprivation. Curr Eye Res 31:947–953
Irie F, Fitzpatrick AL, Lopez OL et al (2008) Enhanced risk for Alzheimer disease in persons with type 2 diabetes and APOE epsilon4: the Cardiovascular Health Study Cognition Study. Arch Neurol 65:89–93
Izumi Y, Yamada KA, Matsukawa M, Zorumski CF (2003) Effects of insulin on long-term potentiation in hippocampal slices from diabetic rats. Diabetologia 46:1007–1012
Jaya Prasanthi RP, Schommer E, Thomasson S, Thompson A, Feist G, Ghribi O (2008) Regulation of beta-amyloid levels in the brain of cholesterol-fed rabbit, a model system for sporadic Alzheimer’s disease. Mech Ageing Dev 129:649–655
Jellinger K, Braak H, Braak E, Fischer P (1991) Alzheimer lesions in the entorhinal region and isocortex in Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s diseases. Ann NY Acad Sci 640:203–209
Killick R, Scales G, Leroy K et al (2009) Deletion of Irs2 reduces amyloid deposition and rescues behavioural deficits in APP transgenic mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 386:257–262
Korczyn AD, Halperin I (2009) Depression and dementia. J Neurol Sci 283:139–142
Kumar P, Kaundal RK, More S, Sharma SS (2009) Beneficial effects of pioglitazone on cognitive impairment in MPTP model of Parkinson’s disease. Behav Brain Res 197:398–403
Kuusisto J, Koivisto K, Mykkanen L et al (1997) Association between features of the insulin resistance syndrome and Alzheimer’s disease independently of apolipoprotein E4 phenotype: cross sectional population based study. BMJ 315:1045–1049
Kyrou I, Tsigos C (2009) Stress hormones: physiological stress and regulation of metabolism. Curr Opin Pharmacol 9:787–793
Labad J, Price JF, Strachan MW et al (2010) Symptoms of depression but not anxiety are associated with central obesity and cardiovascular disease in people with type 2 diabetes: the Edinburgh Type 2 Diabetes Study. Diabetologia. 53:467–471
Landreth G, Jiang Q, Mandrekar S, Heneka M (2008) PPARgamma agonists as therapeutics for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurotherapeutics 5:481–489
Lannert H, Hoyer S (1998) Intracerebroventricular administration of streptozotocin causes long-term diminutions in learning and memory abilities and in cerebral energy metabolism in adult rats. Behav Neurosci 112:1199–1208
Launer LJ (2005) Diabetes and brain aging: epidemiologic evidence. Curr Diab Rep 5:59–63
Laybutt DR, Preston AM, Akerfeldt MC et al (2007) Endoplasmic reticulum stress contributes to beta cell apoptosis in type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia 50:752–763
Leibson CL, Rocca WA, Hanson VA et al (1997) Risk of dementia among persons with diabetes mellitus: a population-based cohort study. Am J Epidemiol 145:301–308
Leonard BE, Myint A (2009) The psychoneuroimmunology of depression. Hum Psychopharmacol 24:165–175
Lin EH, Rutter CM, Katon W et al (2010) Depression and advanced complications of diabetes: a prospective cohort study. Diabetes Care 33:264–269
Lindholm D, Wootz H, Korhonen L (2006) ER stress and neurodegenerative diseases. Cell Death Differ 13:385–392
Lobo A, Launer LJ, Fratiglioni L et al (2000) Prevalence of dementia and major subtypes in Europe: a collaborative study of population-based cohorts. Neurologic Diseases in the Elderly Research Group. Neurology 54:S4–S9
Long-Smith CM, Sullivan AM, Nolan YM (2009) The influence of microglia on the pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease. Prog Neurobiol 89:277–287
Luchsinger JA (2009) Type 2 diabetes, related conditions, and dementia. In: Biessels GJ, Luchsinger JA (eds) Diabetes and the brain. Humana Press, New York, NY, pp 323–342
Luchsinger JA, Gustafson DR (2009) Adiposity, type 2 diabetes, and Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis 16:693–704
Luchsinger JA, Tang MX, Shea S, Mayeux R (2004) Hyperinsulinemia and risk of Alzheimer disease. Neurology 63:1187–1192
Magarinos AM, McEwen BS (2000) Experimental diabetes in rats causes hippocampal dendritic and synaptic reorganization and increased glucocorticoid reactivity to stress. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:11056–11061
McIntyre RS, Rasgon NL, Kemp DE et al (2009) Metabolic syndrome and major depressive disorder: co-occurrence and pathophysiologic overlap. Curr Diab Rep 9:51–59
Medved V, Jovanovic N, Knapic VP (2009) The comorbidity of diabetes mellitus and psychiatric disorders. Psychiatr Danub 21:585–588
Messier C, Teutenberg K (2005) The role of insulin, insulin growth factor, and insulin-degrading enzyme in brain aging and Alzheimer’s disease. Neural Plast 12:311–328
Miller DB, O’Callaghan JP (2008) Do early-life insults contribute to the late-life development of Parkinson and Alzheimer diseases? Metabolism 57(Suppl 2):S44–S49
Moosavi M, Naghdi N, Maghsoudi N, Zahedi Asl S (2006) The effect of intrahippocampal insulin microinjection on spatial learning and memory. Horm Behav 50:748–752
Moran LB, Graeber MB (2008) Towards a pathway definition of Parkinson’s disease: a complex disorder with links to cancer, diabetes and inflammation. Neurogenetics 9:1–13
Moreira PI, Santos MS, Moreno AM, Proenca T, Seica R, Oliveira CR (2004) Effect of streptozotocin-induced diabetes on rat brain mitochondria. J Neuroendocrinol 16:32–38
Moroo I, Yamada T, Makino H et al (1994) Loss of insulin receptor immunoreactivity from the substantia nigra pars compacta neurons in Parkinson’s disease. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 87:343–348
Mosconi L, Nacmias B, Sorbi S et al (2004) Brain metabolic decreases related to the dose of the ApoE e4 allele in Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 75:370–376
Mosconi L, Herholz K, Prohovnik I et al (2005) Metabolic interaction between ApoE genotype and onset age in Alzheimer’s disease: implications for brain reserve. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 76:15–23
Moussavi S, Chatterji S, Verdes E, Tandon A, Patel V, Ustun B (2007) Depression, chronic diseases, and decrements in health: results from the World Health Surveys. Lancet 370:851–858
Muller T, Muhlack S (2008) Impact of endurance exercise on levodopa-associated cortisol release and force increase in patients with Parkinson’s disease. J Neural Transm 115:851–855
Muller T, Welnic J, Muhlack S (2007) Acute levodopa administration reduces cortisol release in patients with Parkinson’s disease. J Neural Transm. 114:347–350
Nielsen SP, Petersen OH (1972) Transport of calcium in the perfused submandibular gland of the cat. J Physiol 223:685–697
Oshitari T, Hata N, Yamamoto S (2008) Endoplasmic reticulum stress and diabetic retinopathy. Vasc Health Risk Manag 4:115–122
Osmanovic J, Plaschke K, Salkovic-Petrisic M, Grünblatt E, Riederer P, Hoyer S (2009) Chronic exogenous corticosterone administration generates an insulin-resistant brain state in rats. Stress 13(2):123–131
Ott A, Stolk RP, Hofman A, van Harskamp F, Grobbee DE, Breteler MM (1996) Association of diabetes mellitus and dementia: the Rotterdam Study. Diabetologia 39:1392–1397
Ott A, Stolk RP, van Harskamp F, Pols HA, Hofman A, Breteler MM (1999) Diabetes mellitus and the risk of dementia: the Rotterdam Study. Neurology 53:1937–1942
Oyadomari S, Takeda K, Takiguchi M et al (2001) Nitric oxide-induced apoptosis in pancreatic beta cells is mediated by the endoplasmic reticulum stress pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:10845–10850
Palade G (1975) Intracellular aspects of the process of protein synthesis. Science 189:867
Pardini AW, Nguyen HT, Figlewicz DP et al (2006) Distribution of insulin receptor substrate-2 in brain areas involved in energy homeostasis. Brain Res 1112:169–178
Park CR, Seeley RJ, Craft S, Woods SC (2000) Intracerebroventricular insulin enhances memory in a passive-avoidance task. Physiol Behav 68:509–514
Passa P (2002) Diabetes trends in Europe. Diabetes Metab Res Rev 18(Suppl 3):S3–S8
Peila R, Rodriguez BL, Launer LJ, Honolulu-Asia Aging S (2002) Type 2 diabetes, APOE gene, and the risk for dementia and related pathologies: the Honolulu-Asia Aging Study. Diabetes 51:1256–1262
Perez A, Morelli L, Cresto JC, Castano EM (2000) Degradation of soluble amyloid beta-peptides 1–40, 1–42, and the Dutch variant 1–40Q by insulin degrading enzyme from Alzheimer disease and control brains. Neurochem Res 25:247–255
Periodical on Aging (1985) Department of International Economic and Social Affairs. United Nations, New York 1:1984
Plaschke K, Kopitz J, Siegelin M et al (2010) Insulin-resistant brain state after intracerebroventricular streptozotocin injection exacerbates Alzheimer-like changes in Tg2576 AbetaPP-overexpressing mice. J Alzheimers Dis 19:691–704
Prichard JS, Schwab RS, Tillmann WA (1951) The effects of stress and the results of medication in different personalities with Parkinson’s disease. Psychosom Med 13:106–111
Quinn LP, Crook B, Hows ME et al (2008) The PPARgamma agonist pioglitazone is effective in the MPTP mouse model of Parkinson’s disease through inhibition of monoamine oxidase B. Br J Pharmacol 154:226–233
Rasgon NL, Kenna HA, Wroolie TE, et al. (Dec 24, 2009) Insulin resistance and hippocampal volume in women at risk for Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging (Epub ahead of print)
Reger MA, Craft S (2006) Intranasal insulin administration: a method for dissociating central and peripheral effects of insulin. Drugs Today (Barc) 42:729–739
Reger MA, Watson GS, Frey WH II et al (2006) Effects of intranasal insulin on cognition in memory-impaired older adults: modulation by APOE genotype. Neurobiol Aging 27:451–458
Reger MA, Watson GS, Green PS et al (2008a) Intranasal insulin administration dose-dependently modulates verbal memory and plasma amyloid-beta in memory-impaired older adults. J Alzheimers Dis 13:323–331
Reger MA, Watson GS, Green PS et al (2008b) Intranasal insulin improves cognition and modulates beta-amyloid in early AD. Neurology 70:440–448
Riedel O, Heuser I, Klotsche J, Dodel R, Wittchen HU, Group GS (2010a) Occurrence risk and structure of depression in Parkinson disease with and without dementia: results from the GEPAD Study. J Geriatr Psychiatry Neurol 23:27–34
Riedel O, Klotsche J, Spottke A, et al. (Feb 6, 2010b) Frequency of dementia, depression, and other neuropsychiatric symptoms in 1,449 outpatients with Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol (Epub ahead of print)
Risner ME, Saunders AM, Altman JF et al (2006) Efficacy of rosiglitazone in a genetically defined population with mild-to-moderate Alzheimer’s disease. Pharmacogenomics J 6:246–254
Ronnemaa E, Zethelius B, Sundelof J et al (2008) Impaired insulin secretion increases the risk of Alzheimer disease. Neurology 71:1065–1071
Ronnemaa E, Zethelius B, Sundelof J et al (2009) Glucose metabolism and the risk of Alzheimer’s disease and dementia: a population-based 12 year follow-up study in 71-year-old men. Diabetologia 52:1504–1510
Ryan CM (2009) Cognition in children and Adolescents with type 1 diabetes. In: Biessels GJ, Luchsinger JA (eds) Diabetes and the brain. Humana Press, New York, NY, pp 251–275
Saczynski JS, White L, Peila RL, Rodriguez BL, Launer LJ (2007) The relation between apolipoprotein A-I and dementia: the Honolulu-Asia aging study. Am J Epidemiol 165:985–992
Salkovic-Petrisic M, Hoyer S (2007) Central insulin resistance as a trigger for sporadic Alzheimer-like pathology: an experimental approach. J Neural Transm Suppl 72:217–233
Salkovic-Petrisic M, Lackovic Z (2003) Intracerebroventricular administration of betacytotoxics alters expression of brain monoamine transporter genes. J Neural Transm 110:15–29
Salkovic-Petrisic M, Tribl F, Schmidt M, Hoyer S, Riederer P (2006) Alzheimer-like changes in protein kinase B and glycogen synthase kinase-3 in rat frontal cortex and hippocampus after damage to the insulin signalling pathway. J Neurochem 96:1005–1015
Sandyk R (1993) The relationship between diabetes mellitus and Parkinson’s disease. Int J Neurosci 69:125–130
Sankar R, Thamotharan S, Shin D, Moley KH, Devaskar SU (2002) Insulin-responsive glucose transporters-GLUT8 and GLUT4 are expressed in the developing mammalian brain. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 107:157–165
Schweitzer I, Tuckwell V, O’Brien J, Ames D (2002) Is late onset depression a prodrome to dementia? Int J Geriatr Psychiatry 17:997–1005
Shoham S, Bejar C, Kovalev E, Weinstock M (2003) Intracerebroventricular injection of streptozotocin causes neurotoxicity to myelin that contributes to spatial memory deficits in rats. Exp Neurol 184:1043–1052
Simon KC, Chen H, Schwarzschild M, Ascherio A (2007) Hypertension, hypercholesterolemia, diabetes, and risk of Parkinson disease. Neurology 69:1688–1695
Slodzinski H, Moran LB, Michael GJ et al (2009) Homocysteine-induced endoplasmic reticulum protein (herp) is up-regulated in parkinsonian substantia nigra and present in the core of Lewy bodies. Clin Neuropathol 28:333–343
Solfrizzi V, Scafato E, Capurso C, et al. (Dec 30 2009) Metabolic syndrome, mild cognitive impairment, and progression to dementia. The Italian Longitudinal Study on Aging. Neurobiol Aging (Epub ahead of print)
Sorrells SF, Caso JR, Munhoz CD, Sapolsky RM (2009) The stressed CNS: when glucocorticoids aggravate inflammation. Neuron 64:33–39
Souza-Talarico JN, Chaves EC, Lupien SJ, Nitrini R, Caramelli P (2010) Relationship between cortisol levels and memory performance may be modulated by the presence or absence of cognitive impairment: evidence from healthy elderly, mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease subjects. J Alzheimers Dis 19:839–848
Stone DK, Reynolds AD, Mosley RL, Gendelman HE (2009) Innate and adaptive immunity for the pathobiology of Parkinson’s disease. Antioxid Redox Signal 11:2151–2166
Sun X, Steffens DC, Au R et al (2008) Amyloid-associated depression: a prodromal depression of Alzheimer disease? Arch Gen Psychiatry 65:542–550
Supnet C, Bezprozvanny I (2010) The dysregulation of intracellular calcium in Alzheimer disease. Cell Calcium 47(2):183–189 Epub 2010 Jan 18
Swaab DF, Chung WC, Kruijver FP, Hofman MA, Hestiantoro A (2003) Sex differences in the hypothalamus in the different stages of human life. Neurobiol Aging 24(Suppl 1):S1–S16 discussion S17–S19
Swaab DF, Bao AM, Lucassen PJ (2005) The stress system in the human brain in depression and neurodegeneration. Ageing Res Rev 4:141–194
Takahashi M, Yamada T, Tooyama I et al (1996) Insulin receptor mRNA in the substantia nigra in Parkinson’s disease. Neurosci Lett 204:201–204
Todes CJ, Lees AJ (1985) The pre-morbid personality of patients with Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 48:97–100
Tong Y, Shen J (2009) alpha-Synuclein and LRRK2: partners in crime. Neuron 64:771–773
Tong M, Neusner A, Longato L, Lawton M, Wands JR, de la Monte SM (2009) Nitrosamine exposure causes insulin resistance diseases: relevance to type 2 diabetes mellitus, non-alcoholic steatohepatitis, and Alzheimer’s disease. Mol Neurodegener 4:54
Tyrovolas S, Lionis C, Zeimbekis A et al (2009) Increased body mass and depressive symptomatology are associated with hypercholesterolemia, among elderly individuals; results from the MEDIS study. Lipids Health Dis 8:10
Unger JW, Livingston JN, Moss AM (1991) Insulin receptors in the central nervous system: localization, signalling mechanisms and functional aspects. Prog Neurobiol 36:343–362
van den Berg E, Reijmer YD, Biessels GJ (2009) Cognition in type 2 diabetes or pre-diabetic stages. In: Biessels GJ, Luchsinger JA (eds) Diabetes and the brain. Humana Press, New York, NY, pp 295–322
Watson GS, Craft S (2003) The role of insulin resistance in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease: implications for treatment. CNS Drugs 17:27–45
Watson GS, Peskind ER, Asthana S et al (2003) Insulin increases CSF Abeta42 levels in normal older adults. Neurology 60:1899–1903
Watson GS, Cholerton BA, Reger MA et al (2005) Preserved cognition in patients with early Alzheimer disease and amnestic mild cognitive impairment during treatment with rosiglitazone: a preliminary study. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry 13:950–958
Watson GS, Bernhardt T, Reger MA et al (2006) Insulin effects on CSF norepinephrine and cognition in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 27:38–41
Whitmer RA (2007) Type 2 diabetes and risk of cognitive impairment and dementia. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep 7:373–380
Whitmer RA, Gustafson DR, Barrett-Connor E, Haan MN, Gunderson EP, Yaffe K (2008) Central obesity and increased risk of dementia more than three decades later. Neurology 71:1057–1064
Woods SC, Seeley RJ, Baskin DG, Schwartz MW (2003) Insulin and the blood-brain barrier. Curr Pharm Des 9:795–800
Wozniak M, Rydzewski B, Baker SP, Raizada MK (1993) The cellular and physiological actions of insulin in the central nervous system. Neurochem Int 22:1–10
Wurtman RJ (2005) Genes, stress, and depression. Metabolism 54:16–19
Zeevalk GD, Bernard LP, Sinha C, Ehrhart J, Nicklas WJ (1998) Excitotoxicity and oxidative stress during inhibition of energy metabolism. Dev Neurosci 20:444–453
Zhong N, Ramaswamy G, Weisgraber KH (2009) Apolipoprotein E4 domain interaction induces endoplasmic reticulum stress and impairs astrocyte function. J Biol Chem 284:27273–27280
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Riederer, P., Bartl, J., Laux, G. et al. Diabetes Type II: A Risk Factor for Depression–Parkinson–Alzheimer?. Neurotox Res 19, 253–265 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-010-9203-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-010-9203-1