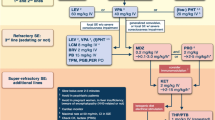
Abstract
Status epilepticus (SE) treatment strategies vary substantially from one institution to another due to the lack of data to support one treatment over another. To provide guidance for the acute treatment of SE in critically ill patients, the Neurocritical Care Society organized a writing committee to evaluate the literature and develop an evidence-based and expert consensus practice guideline. Literature searches were conducted using PubMed and studies meeting the criteria established by the writing committee were evaluated. Recommendations were developed based on the literature using standardized assessment methods from the American Heart Association and Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development, and Evaluation systems, as well as expert opinion when sufficient data were lacking.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beran RG. An alternative perspective on the management of status epilepticus. Epilepsy Behav. 2008;12(3):349–53.
Seif-Eddeine H, Treiman DM. Problems and controversies in status epilepticus: a review and recommendations. Expert Rev Neurother. 2011;11(12):1747–58.
Rossetti AO, Lowenstein DH. Management of refractory status epilepticus in adults: still more questions than answers. Lancet Neurol. 2011;10(10):922–30.
Gibbons RJ, Smith S, Antman E. American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association clinical practice guidelines: Part I: where do they come from? Circulation. 2003;107(23):2979–86.
Jaeschke R, Guyatt GH, Dellinger P, Schunemann H, Levy MM, Kunz R, Norris S, Bion J. Use of GRADE grid to reach decisions on clinical practice guidelines when consensus is elusive. BMJ. 2008;337:a744.
Abend NS, Dlugos DJ, Hahn CD, Hirsch LJ, Herman ST. Use of EEG monitoring and management of non-convulsive seizures in critically ill patients: a survey of neurologists. Neurocrit Care. 2010;12(3):382–9.
Jenssen S, Gracely EJ, Sperling MR. How long do most seizures last? A systematic comparison of seizures recorded in the epilepsy monitoring unit. Epilepsia. 2006;47(9):1499–503.
Lowenstein DH. Current concepts: status epilepticus. N Engl J Med. 1998;338(14):970.
Theodore WH, Porter RJ, Albert P, Kelley K, Bromfield E, Devinsky O, Sato S. The secondarily generalized tonic-clonic seizure: a videotape analysis. Neurology. 1994;44(8):1403–7.
Shinnar S. How long do new-onset seizures in children last? Ann Neurol. 2001;49(5):659–64.
Meldrum BS, Horton RW. Physiology of status epilepticus in primates. Arch Neurol. 1973;28(1):1–9.
Chen JWY, Wasterlain CG. Status epilepticus: pathophysiology and management in adults. Lancet Neurol. 2006;5(3):246–56.
Kapur J. Rapid seizure-induced reduction of benzodiazepine and Zn2 sensitivity of hippocampal dentate granule cell GABAA receptors. J Neurosci. 1997;17(19):7532.
Mazarati AM. Time-dependent decrease in the effectiveness of antiepileptic drugs during the course of self-sustaining status epilepticus. Brain Res. 1998;814(1–2):179.
Hirsch LJ. Status epilepticus. CONTINUUM Lifelong Learn Neurol. 2007;13(4):121–51.
Lowenstein DH. Status epilepticus: an overview of the clinical problem. Epilepsia. 1999;40(Suppl 1):S3–8. discussion S21–22.
Meldrum BS. The revised operational definition of generalised tonic-clonic (TC) status epilepticus in adults. Epilepsia. 1999;40(1):123–4.
Knake S, Hamer HM, Rosenow F. Status epilepticus: a critical review. Epilepsy Behav. 2009;15(1):10–4.
Alldredge BK. A comparison of lorazepam, diazepam, and placebo for the treatment of out-of-hospital status epilepticus. N Engl J Med. 2001;345(9):631–7.
Meierkord H, Boon P, Engelsen B, Göcke K, Shorvon S, Tinuper P, Holtkamp M. EFNS guideline on the management of status epilepticus. Eur J Neurol. 2006;13(5):445–50.
Walker M. Status epilepticus: an evidence based guide. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed). 2005;331(7518):673–7.
Shorvon S. The management of status epilepticus. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2001;70(Suppl 2):22–7.
Kaplan PW. Nonconvulsive status epilepticus in the emergency room. Epilepsia. 1996;37(7):643–50.
Shorvon S. What is nonconvulsive status epilepticus, and what are its subtypes? Epilepsia. 2007;48(Suppl 8):35–8.
Towne AR, Waterhouse EJ, Boggs JG, Garnett LK, Brown AJ, Smith JR Jr, DeLorenzo RJ. Prevalence of nonconvulsive status epilepticus in comatose patients. Neurology. 2000;54(2):340–5.
Rossetti AO, Reichhart MD, Schaller MD, Despland PA, Bogousslavsky J. Propofol treatment of refractory status epilepticus: a study of 31 episodes. Epilepsia. 2004;45(7):757–63.
Krishnamurthy KB, Drislane FW. Depth of EEG suppression and outcome in barbiturate anesthetic treatment for refractory status epilepticus. Epilepsia. 1999;40(6):759–62.
Claassen J, Hirsch LJ, Emerson RG, Bates JE, Thompson TB, Mayer SA. Continuous EEG monitoring and midazolam infusion for refractory nonconvulsive status epilepticus. Neurology. 2001;57(6):1036–42.
Arif H. Treatment of status epilepticus. Semin Neurol. 2008;28(03):342–54.
Treiman DM, Meyers PD, Walton NY, Collins JF, Colling C, Rowan AJ, Handforth A, Faught E, Calabrese VP, Uthman BM, et al. A comparison of four treatments for generalized convulsive status epilepticus. Veterans affairs status epilepticus cooperative study group. N Engl J Med. 1998;339(12):792–8.
Jirsch J, Hirsch LJ. Nonconvulsive seizures: developing a rational approach to the diagnosis and management in the critically ill population. Clin Neurophysiol. 2007;118(8):1660–70.
Bleck TP. Refractory status epilepticus. Curr Opin Crit care. 2005;11(2):117–20.
Shinnar S, Pellock JM, Moshe SL, Maytal J, O’Dell C, Driscoll SM, Alemany M, Newstein D, DeLorenzo RJ. In whom does status epilepticus occur: age-related differences in children. Epilepsia. 1997;38(8):907–14.
Chin RF, Neville BG, Peckham C, Bedford H, Wade A, Scott RC. Incidence, cause, and short-term outcome of convulsive status epilepticus in childhood: prospective population-based study. Lancet. 2006;368(9531):222–9.
Riviello JJ, Ashwal S, Hirtz D, Glauser T, Ballaban-Gil K, Kelley K, Morton LD, Phillips S, Sloan E, Shinnar S. Practice parameter: diagnostic assessment of the child with status epilepticus (an evidence-based review). Neurology. 2006;67(9):1542–50.
Claassen J, Lokin JK, Fitzsimmons BF, Mendelsohn FA, Mayer SA. Predictors of functional disability and mortality after status epilepticus. Neurology. 2002;58(1):139–42.
Rossetti AO, Hurwitz S, Logroscino G, Bromfield EB. Prognosis of status epilepticus: role of aetiology, age, and consciousness impairment at presentation. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2006;77(5):611–5.
Novy J, Rossetti AO. Oral pregabalin as an add-on treatment for status epilepticus. Epilepsia. 2010;51(10):2207–10.
Logroscino G, Hesdorffer DC, Cascino G, Annegers JF, Hauser WA. Short-term mortality after a first episode of status epilepticus. Epilepsia. 1997;38(12):1344–9.
Legriel S, Mourvillier B, Bele N, Amaro J, Fouet P, Manet P, Hilpert F. Outcomes in 140 critically ill patients with status epilepticus. Intensive Care Med. 2008;34(3):476–80.
Legriel S. Functional outcome after convulsive status epilepticus. Crit Care Med. 2010;38(12):2295–303.
Logroscino G, Hesdorffer DC, Cascino GD, Annegers JF, Bagiella E, Hauser WA. Long-term mortality after a first episode of status epilepticus. Neurology. 2002;58(4):537–41.
Riviello JJ, Holmes GL. The treatment of status epilepticus. Semin Pediatr Neurol. 2004;11(2):129–38.
Oxbury JM. Causes and consequences of status epilepticus in adults. A study of 86 cases. Brain. 1971;94(4):733–44.
Aminoff MJ, Simon RP. Status epilepticus: causes, clinical features and consequences in 98 patients. Am J Med. 1980;69(5):657–66.
Lowenstein DH, Alldredge BK. Status epilepticus at an urban public hospital in the 1980s. Neurology. 1993;43(3 Pt 1):483–8.
Scholtes FB, Renier WO, Meinardi H. Generalized convulsive status epilepticus: causes, therapy, and outcome in 346 patients. Epilepsia. 1994;35(5):1104–12.
Logroscino G, Hesdorffer DC, Cascino G, Annegers JF, Hauser WA. Time trends in incidence, mortality, and case-fatality after first episode of status epilepticus. Epilepsia. 2001;42(8):1031–5.
Delanty N, French JA, Labar DR, Pedley TA, Rowan AJ. Status epilepticus arising de novo in hospitalized patients: an analysis of 41 patients. Seizure. 2001;10(2):116–9.
Aranda A, Foucart G, Ducassé JL, Grolleau S, McGonigal A, Valton L. Generalized convulsive status epilepticus management in adults: a cohort study with evaluation of professional practice. Epilepsia. 2010;51(10):2159–67.
Young B, Jordan K, Doig G. An assessment of nonconvulsive seizures in the intensive care unit using continuous EEG monitoring: an investigation of variables associated with mortality. Neurology. 1996;47:83–9.
Litt B, Wityk RJ, Hertz SH, Mullen PD, Weiss H, Ryan DD, Henry TR. Nonconvulsive status epilepticus in the critically ill elderly. Epilepsia. 1998;39(11):1194–202.
Shneker BF, Fountain NB. Assessment of acute morbidity and mortality in nonconvulsive status epilepticus. Neurology. 2003;61(8):1066–73.
DeLorenzo RJ, Waterhouse EJ, Towne AR, Boggs JG, Ko D, DeLorenzo GA, Brown A, Garnett L. Persistent nonconvulsive status epilepticus after the control of convulsive status epilepticus. Epilepsia. 1998;39(8):833–40.
Young GB, Blume WT, Bolton CF, Warren KG. Anesthetic barbiturates in refractory status epilepticus. Can J Neurol Sci. 1980;7(4):291–2.
Rashkin MC, Youngs C, Penovich P. Pentobarbital treatment of refractory status epilepticus. Neurology. 1987;37(3):500.
Osorio I, Reed RC. Treatment of refractory generalized tonic-clonic status epilepticus with pentobarbital anesthesia after high-dose phenytoin. Epilepsia. 1989;30(4):464–71.
Van Ness PC. Pentobarbital and EEG burst suppression in treatment of status epilepticus refractory to benzodiazepines and phenytoin. Epilepsia. 1990;31(1):61–7.
Yaffe K, Lowenstein DH. Prognostic factors of pentobarbital therapy for refractory generalized status epilepticus. Neurology. 1993;43(5):895.
Sagduyu A, Tarlaci S, Sirin H. Generalized tonic-clonic status epilepticus: causes, treatment, complications and predictors of case fatality. J Neurol. 1998;245(10):640–6.
Brown L. Role of propofol in refractory status epilepticus. Ann Pharmacother. 1998;32(10):1053–9.
Stecker MM, Kramer TH, Raps EC, O’Meeghan R, Dulaney E, Skaar DJ. Treatment of refractory status epilepticus with propofol: clinical and pharmacokinetic findings. Epilepsia. 1998;39(1):18–26.
Claassen J, Hirsch LJ, Emerson RG, Mayer SA. Treatment of refractory status epilepticus with pentobarbital, propofol, or midazolam: a systematic review. Epilepsia. 2002;43(2):146–53.
Drislane FW, Blum AS, Lopez MR, Gautam S, Schomer DL. Duration of refractory status epilepticus and outcome: loss of prognostic utility after several hours. Epilepsia. 2009;50(6):1566–71.
Holtkamp M, Othman J, Buchheim K, Meierkord H. Predictors and prognosis of refractory status epilepticus treated in a neurological intensive care unit. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2005;76(4):534–9.
Rossetti AO, Logroscino G, Bromfield EB. Refractory status epilepticus: effect of treatment aggressiveness on prognosis. Arch Neurol. 2005;62(11):1698–702.
Drislane FW, Lopez MR, Blum AS, Schomer DL. Detection and treatment of refractory status epilepticus in the intensive care unit. J Clin Neurophysiol. 2008;25(4):181–6.
Rossetti AO, Milligan TA, Vulliemoz S, Michaelides C, Bertschi M, Lee JW. A randomized trial for the treatment of refractory status epilepticus. Neurocrit Care. 2011;14(1):4–10.
Saz EU, Karapinar B, Ozcetin M, Polat M, Tosun A, Serdaroglu G, Gokben S, Tekgul H. Convulsive status epilepticus in children: etiology, treatment protocol and outcome. Seizure. 2011;20(2):115–8.
Sahin M, Menache CC, Holmes GL, Riviello JJ. Outcome of severe refractory status epilepticus in children. Epilepsia. 2001;42(11):1461–7.
Sahin M, Menache CC, Holmes GL, Riviello JJ. Prolonged treatment for acute symptomatic refractory status epilepticus. Neurology. 2003;61(3):398–401.
Gilbert DL, Gartside PS, Glauser TA. Efficacy and mortality in treatment of refractory generalized convulsive status epilepticus in children: a meta-analysis. J Child Neurol. 1999;14(9):602–9.
Mayer SA, Claassen J, Lokin J, Mendelsohn F, Dennis LJ, Fitzsimmons B-F. Refractory status epilepticus: frequency, risk factors, and impact on outcome. Arch Neurol. 2002;59(2):205–10.
Maytal J, Shinnar S, Moshé SL, Alvarez LA. Low morbidity and mortality of status epilepticus in children. Pediatrics. 1989;83(3):323–31.
Towne AR, Pellock JM, Ko D, DeLorenzo RJ. Determinants of mortality in status epilepticus. Epilepsia. 1994;35(1):27–34.
Lewena S, Pennington V, Acworth J, Thornton S, Ngo P, McIntyre S, Krieser D, Neutze J, Speldewinde D. Emergency management of pediatric convulsive status epilepticus: a multicenter study of 542 patients. Pediatr Emerg Care. 2009;25(2):83–7.
Roppolo LP, Walters K. Airway management in neurological emergencies. Neurocrit Care. 2004;1(4):405–14.
van Rijckevorsel K, Boon P, Hauman H, Legros B, Ossemanns M, Sadzot B, Schmedding E, van Zandijcke M. Standards of care for adults with convulsive status epilepticus: Belgian consensus recommendations. Acta Neurol Belg. 2005;105(3):111–8.
Varelas PN, Mirski MA. Status epilepticus. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2009;9(6):469–76.
Privitera M, Hoffman M, Moore JL, Jester D. EEG detection of nontonic-clonic status epilepticus in patients with altered consciousness. Epilepsy Res. 1994;18(2):155–66.
Drislane FW. Presentation, evaluation, and treatment of nonconvulsive status epilepticus. Epilepsy Behav. 2000;1(5):301–14.
Oddo M, Carrera E, Claassen J, Mayer SA, Hirsch LJ. Continuous electroencephalography in the medical intensive care unit. Crit Care Med. 2009;37(6):2051–6.
Leppik IE, Derivan AT, Homan RW, Walker J, Ramsay RE, Patrick B. Double-blind study of lorazepam and diazepam in status epilepticus. JAMA. 1983;249(11):1452–4.
Silbergleit R, Durkalski V, Lowenstein D, Conwit R, Pancioli A, Palesch Y, Barsan W. Intramuscular versus intravenous therapy for prehospital status epilepticus. N Engl J Med. 2012;366(7):591–600.
Alvarez N, Besag F, Iivanainen M. Use of antiepileptic drugs in the treatment of epilepsy in people with intellectual disability. J Intellect Disabil Res. 1998;42(Suppl 1):1–15.
Troester MM, Hastriter EV, Ng YT. Dissolving oral clonazepam wafers in the acute treatment of prolonged seizures. J Child Neurol. 2010;25(12):1468–72.
Treiman DM, Walker MC. Treatment of seizure emergencies: convulsive and non-convulsive status epilepticus. Epilepsy Res. 2006;68(Suppl 1):S77–82.
Appleton R, Sweeney A, Choonara I, Robson J, Molyneux E. Lorazepam versus diazepam in the acute treatment of epileptic seizures and status epilepticus. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1995;37(8):682–8.
Walker JE, Homan RW, Vasko MR, Crawford IL, Bell RD, Tasker WG. Lorazepam in status epilepticus. Ann Neurol. 1979;6(3):207–13.
Cock HR, Schapira AH. A comparison of lorazepam and diazepam as initial therapy in convulsive status epilepticus. QJM. 2002;95(4):225–31.
Crawford TO, Mitchell WG, Snodgrass SR. Lorazepam in childhood status epilepticus and serial seizures: effectiveness and tachyphylaxis. Neurology. 1987;37(2):190–5.
Kapur J. Prehospital treatment of status epilepticus with benzodiazepines is effective and safe. Epilepsy Curr. 2002;2(4):121–4.
Treiman DM. Treatment of convulsive status epilepticus. Int Rev Neurobiol. 2007;81:273–85.
Prasad K, Krishnan PR, Al-Roomi K, Sequeira R. Anticonvulsant therapy for status epilepticus. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2007;63(6):640–7.
Giang DW, McBride MC. Lorazepam versus diazepam for the treatment of status epilepticus. Pediatr Neurol. 1988;4(6):358–61.
Labar DR, Ali A, Root J. High-dose intravenous lorazepam for the treatment of refractory status epilepticus. Neurology. 1994;44(8):1400–3.
Sreenath TG, Gupta P, Sharma KK, Krishnamurthy S. Lorazepam versus diazepam-phenytoin combination in the treatment of convulsive status epilepticus in children: a randomized controlled trial. Eur J Paediatr Neurol. 2010;14(2):162–8.
Qureshi A, Wassmer E, Davies P, Berry K, Whitehouse WP. Comparative audit of intravenous lorazepam and diazepam in the emergency treatment of convulsive status epilepticus in children. Seizure. 2002;11(3):141–4.
McMullan J, Sasson C, Pancioli A, Silbergleit R. Midazolam versus diazepam for the treatment of status epilepticus in children and young adults: a meta-analysis. Acad Emerg Med. 2010;17(6):575–82.
Nakken KO, Lossius MI. Buccal midazolam or rectal diazepam for treatment of residential adult patients with serial seizures or status epilepticus. Acta Neurol Scand. 2011;124(2):99–103.
Baysun S, Aydin OF, Atmaca E, Gurer YK. A comparison of buccal midazolam and rectal diazepam for the acute treatment of seizures. Clin Pediatr (Phila). 2005;44(9):771–6.
Lahat E, Goldman M, Barr J, Bistritzer T, Berkovitch M. Comparison of intranasal midazolam with intravenous diazepam for treating febrile seizures in children: prospective randomised study. BMJ. 2000;321(7253):83–6.
McIntyre J, Robertson S, Norris E, Appleton R, Whitehouse WP, Phillips B, Martland T, Berry K, Collier J, Smith S, et al. Safety and efficacy of buccal midazolam versus rectal diazepam for emergency treatment of seizures in children: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2005;366(9481):205–10.
Scott RC, Besag FM, Neville BG. Buccal midazolam and rectal diazepam for treatment of prolonged seizures in childhood and adolescence: a randomised trial. Lancet. 1999;353(9153):623–6.
Mahmoudian T, Zadeh MM. Comparison of intranasal midazolam with intravenous diazepam for treating acute seizures in children. Epilepsy Behav. 2004;5(2):253–5.
Yoshikawa H, Yamazaki S, Abe T, Oda Y. Midazolam as a first-line agent for status epilepticus in children. Brain Dev. 2000;22(4):239–42.
Brevoord JC, Joosten KF, Arts WF, van Rooij RW, de Hoog M. Status epilepticus: clinical analysis of a treatment protocol based on midazolam and phenytoin. J Child Neurol. 2005;20(6):476–81.
Koul RL, Raj Aithala G, Chacko A, Joshi R, Elbualy M. Continuous midazolam infusion as treatment of status epilepticus. Arch Dis Child. 1997;76(5):445–8.
Nicol CF, Tutton JC, Smith BH. Parenteral diazepam in status epilepticus. Neurology. 1969;19(4):332–43.
Parsonage MJ, Norris JW. Use of diazepam in treatment of severe convulsive status epilepticus. Br Med J. 1967;3(5557):85–8.
Dieckmann RA. Rectal diazepam for prehospital pediatric status epilepticus. Ann Emerg Med. 1994;23(2):216–24.
McMorris S, McWilliam PK. Status epilepticus in infants and young children treated with parenteral diazepam. Arch Dis Child. 1969;44(237):604–11.
Lombroso CT. Treatment of status epilepticus with diazepam. Neurology. 1966;16(7):629–34.
Shaner DM, McCurdy SA, Herring MO, Gabor AJ. Treatment of status epilepticus: a prospective comparison of diazepam and phenytoin versus phenobarbital and optional phenytoin. Neurology. 1988;38(2):202–7.
Sugai K. Treatment of convulsive status epilepticus in infants and young children in Japan. Acta Neurol Scand Suppl. 2007;186:62–70.
Gilad R, Izkovitz N, Dabby R, Rapoport A, Sadeh M, Weller B, Lampl Y. Treatment of status epilepticus and acute repetitive seizures with i.v. valproic acid vs phenytoin. Acta Neurol Scand. 2008;118(5):296–300.
Misra UK, Kalita J, Patel R. Sodium valproate vs phenytoin in status epilepticus: a pilot study. Neurology. 2006;67(2):340–2.
Prasad K, Al-Roomi K, Krishnan PR, Sequeira R: Anticonvulsant therapy for status epilepticus. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2005(4):CD003723.
Swisher CB, Doreswamy M, Gingrich KJ, Vredenburgh JJ, Kolls BJ. Phenytoin, levetiracetam, and pregabalin in the acute management of refractory status epilepticus in patients with brain tumors. Neurocrit Care. 2011;16(1):109–13.
Limdi NA, Shimpi AV, Faught E, Gomez CR, Burneo JG. Efficacy of rapid IV administration of valproic acid for status epilepticus. Neurology. 2005;64(2):353–5.
Giroud M. Use of injectable valproic acid in status epilepticus: a pilot study. Clinical Drug Investig. 1993;5:154.
Peters CN, Pohlmann-Eden B. Intravenous valproate as an innovative therapy in seizure emergency situations including status epilepticus: experience in 102 adult patients. Seizure. 2005;14(3):164–9.
Berning S, Boesebeck F, van Baalen A, Kellinghaus C. Intravenous levetiracetam as treatment for status epilepticus. J Neurol. 2009;256(10):1634–42.
Eue S, Grumbt M, Muller M, Schulze A. Two years of experience in the treatment of status epilepticus with intravenous levetiracetam. Epilepsy Behav. 2009;15(4):467–9.
Beyenburg S, Reuber M, Maraite N. Intravenous levetiracetam for epileptic seizure emergencies in older people. Gerontology. 2009;55(1):27–31.
Ruegg S, Naegelin Y, Hardmeier M, Winkler DT, Marsch S, Fuhr P. Intravenous levetiracetam: treatment experience with the first 50 critically ill patients. Epilepsy Behav. 2008;12(3):477–80.
Rupprecht S, Franke K, Fitzek S, Witte OW, Hagemann G. Levetiracetam as a treatment option in non-convulsive status epilepticus. Epilepsy Res. 2007;73(3):238–44.
Fattouch J, Di Bonaventura C, Casciato S, Bonini F, Petrucci S, Lapenta L, Manfredi M, Prencipe M, Giallonardo AT. Intravenous levetiracetam as first-line treatment of status epilepticus in the elderly. Acta Neurol Scand. 2010;121(6):418–21.
Abend NS, Monk HM, Licht DJ, Dlugos DJ. Intravenous levetiracetam in critically ill children with status epilepticus or acute repetitive seizures. Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2009;10(4):505–10.
Uges JW, van Huizen MD, Engelsman J, Wilms EB, Touw DJ, Peeters E, Vecht CJ. Safety and pharmacokinetics of intravenous levetiracetam infusion as add-on in status epilepticus. Epilepsia. 2009;50(3):415–21.
Yu KT, Mills S, Thompson N, Cunanan C. Safety and efficacy of intravenous valproate in pediatric status epilepticus and acute repetitive seizures. Epilepsia. 2003;44(5):724–6.
Agarwal P, Kumar N, Chandra R, Gupta G, Antony AR, Garg N. Randomized study of intravenous valproate and phenytoin in status epilepticus. Seizure. 2007;16(6):527–32.
Alvarez V, Januel JM, Burnand B, Rossetti AO. Second-line status epilepticus treatment: comparison of phenytoin, valproate, and levetiracetam. Epilepsia. 2011;52(7):1292–6.
Chen L, Feng P, Wang J, Liu L, Zhou D. Intravenous sodium valproate in mainland China for the treatment of diazepam refractory convulsive status epilepticus. J Clin Neurosci. 2009;16(4):524–6.
Olsen KB, Tauboll E, Gjerstad L. Valproate is an effective, well-tolerated drug for treatment of status epilepticus/serial attacks in adults. Acta Neurol Scand Suppl. 2007;187:51–4.
Sinha S, Naritoku DK. Intravenous valproate is well tolerated in unstable patients with status epilepticus. Neurology. 2000;55(5):722–4.
Chin RF, Neville BG, Peckham C, Wade A, Bedford H, Scott RC. Treatment of community-onset, childhood convulsive status epilepticus: a prospective, population-based study. Lancet Neurol. 2008;7(8):696–703.
Crawford TO, Mitchell WG, Fishman LS, Snodgrass SR. Very-high-dose phenobarbital for refractory status epilepticus in children. Neurology. 1988;38(7):1035–40.
Lowenstein DH, Aminoff MJ, Simon RP. Barbiturate anesthesia in the treatment of status epilepticus: clinical experience with 14 patients. Neurology. 1988;38(3):395–400.
Moddel G, Bunten S, Dobis C, Kovac S, Dogan M, Fischera M, Dziewas R, Schabitz WR, Evers S, Happe S. Intravenous levetiracetam: a new treatment alternative for refractory status epilepticus. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2009;80(6):689–92.
Gamez-Leyva G, Aristin JL, Fernandez E, Pascual J. Experience with intravenous levetiracetam in status epilepticus: a retrospective case series. CNS Drugs. 2009;23(11):983–7.
Singhi S, Murthy A, Singhi P, Jayashree M. Continuous midazolam versus diazepam infusion for refractory convulsive status epilepticus. J Child Neurol. 2002;17(2):106–10.
Ozdemir D, Gulez P, Uran N, Yendur G, Kavakli T, Aydin A. Efficacy of continuous midazolam infusion and mortality in childhood refractory generalized convulsive status epilepticus. Seizure. 2005;14(2):129–32.
Prasad A, Worrall BB, Bertram EH, Bleck TP. Propofol and midazolam in the treatment of refractory status epilepticus. Epilepsia. 2001;42(3):380–6.
Ulvi H, Yoldas T, Mungen B, Yigiter R. Continuous infusion of midazolam in the treatment of refractory generalized convulsive status epilepticus. Neurol Sci. 2002;23(4):177–82.
Rivera R, Segnini M, Baltodano A, Perez V. Midazolam in the treatment of status epilepticus in children. Crit Care Med. 1993;21(7):991–4.
Kumar A, Bleck TP. Intravenous midazolam for the treatment of refractory status epilepticus. Crit Care Med. 1992;20(4):483–8.
Koul R, Chacko A, Javed H, Al Riyami K. Eight-year study of childhood status epilepticus: midazolam infusion in management and outcome. J Child Neurol. 2002;17(12):908–10.
Igartua J, Silver P, Maytal J, Sagy M. Midazolam coma for refractory status epilepticus in children. Crit Care Med. 1999;27(9):1982–5.
Morrison G, Gibbons E, Whitehouse WP. High-dose midazolam therapy for refractory status epilepticus in children. Intensive Care Med. 2006;32(12):2070–6.
Cornfield DN, Tegtmeyer K, Nelson MD, Milla CE, Sweeney M. Continuous propofol infusion in 142 critically ill children. Pediatrics. 2002;110(6):1177–81.
Fong JJ, Sylvia L, Ruthazer R, Schumaker G, Kcomt M, Devlin JW. Predictors of mortality in patients with suspected propofol infusion syndrome. Crit Care Med. 2008;36(8):2281–7.
Parviainen I, Uusaro A, Kalviainen R, Mervaala E, Ruokonen E. Propofol in the treatment of refractory status epilepticus. Intensive Care Med. 2006;32(7):1075–9.
van Gestel JP, Blusse van Oud-Alblas HJ, Malingre M, Ververs FF, Braun KP, van Nieuwenhuizen O. Propofol and thiopental for refractory status epilepticus in children. Neurology. 2005;65(4):591–2.
Iyer VN, Hoel R, Rabinstein AA. Propofol infusion syndrome in patients with refractory status epilepticus: an 11-year clinical experience. Crit Care Med. 2009;37(12):3024–30.
Krishnamurthy KB, Drislane FW. Relapse and survival after barbiturate anesthetic treatment of refractory status epilepticus. Epilepsia. 1996;37(9):863–7.
ter Maaten JC, Strack van Schijndel RJ, Heimans JJ, Schreuder WO. Ten patients with refractory status epilepticus in an intensive care department. Neth J Med. 1998;53(6):260–5.
Partinen M, Kovanen J, Nilsson E. Status epilepticus treated by barbiturate anaesthesia with continuous monitoring of cerebral function. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed). 1981;282(6263):520–1.
Tripathi M, Vibha D, Choudhary N, Prasad K, Srivastava MV, Bhatia R, Chandra SP. Management of refractory status epilepticus at a tertiary care centre in a developing country. Seizure. 2010;19(2):109–11.
Mehta V, Singhi P, Singhi S. Intravenous sodium valproate versus diazepam infusion for the control of refractory status epilepticus in children: a randomized controlled trial. J Child Neurol. 2007;22(10):1191–7.
Uberall MA, Trollmann R, Wunsiedler U, Wenzel D. Intravenous valproate in pediatric epilepsy patients with refractory status epilepticus. Neurology. 2000;54(11):2188–9.
Knake S, Gruener J, Hattemer K, Klein KM, Bauer S, Oertel WH, Hamer HM, Rosenow F. Intravenous levetiracetam in the treatment of benzodiazepine refractory status epilepticus. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2008;79(5):588–9.
Patel NC, Landan IR, Levin J, Szaflarski J, Wilner AN. The use of levetiracetam in refractory status epilepticus. Seizure. 2006;15(3):137–41.
Gallentine WB, Hunnicutt AS, Husain AM. Levetiracetam in children with refractory status epilepticus. Epilepsy Behav. 2009;14(1):215–8.
Miyahara A, Saito Y, Sugai K, Nakagawa E, Sakuma H, Komaki H, Sasaki M. Reassessment of phenytoin for treatment of late stage progressive myoclonus epilepsy complicated with status epilepticus. Epilepsy Res. 2009;84(2–3):201–9.
Albers JM, Moddel G, Dittrich R, Steidl C, Suntrup S, Ringelstein EB, Dziewas R. Intravenous lacosamide: an effective add-on treatment of refractory status epilepticus. Seizure. 2011;20(5):428–30.
Goodwin H, Hinson HE, Shermock KM, Karanjia N, Lewin JJ 3rd. The use of lacosamide in refractory status epilepticus. Neurocrit Care. 2011;14(3):348–53.
Kellinghaus C, Berning S, Immisch I, Larch J, Rosenow F, Rossetti AO, Tilz C, Trinka E. Intravenous lacosamide for treatment of status epilepticus. Acta Neurol Scand. 2011;123(2):137–41.
Towne AR, Garnett LK, Waterhouse EJ, Morton LD, DeLorenzo RJ. The use of topiramate in refractory status epilepticus. Neurology. 2003;60(2):332–4.
Shearer P, Riviello J. Generalized convulsive status epilepticus in adults and children: treatment guidelines and protocols. Emerg Med Clin North Am. 2011;29(1):51–64.
Rossetti AO. Which anesthetic should be used in the treatment of refractory status epilepticus? Epilepsia. 2007;48(Suppl 8):52–5.
Shorvon S, Ferlisi M. The treatment of super-refractory status epilepticus: a critical review of available therapies and a clinical treatment protocol. Brain. 2011;134(Pt 10):2802–18.
Cooper AD, Britton JW, Rabinstein AA. Functional and cognitive outcome in prolonged refractory status epilepticus. Arch Neurol. 2009;66(12):1505–9.
Lee WK, Liu KT, Young BW. Very-high-dose phenobarbital for childhood refractory status epilepticus. Pediatr Neurol. 2006;34(1):63–5.
Mirski MA, Williams MA, Hanley DF. Prolonged pentobarbital and phenobarbital coma for refractory generalized status epilepticus. Crit Care Med. 1995;23(2):400–4.
Bramstedt KA, Morris HH, Tanner A. Now we lay them down to sleep: ethical issues with the use of pharmacologic coma for adult status epilepticus. Epilepsy Behav. 2004;5(5):752–5.
Dara SI, Tungpalan LA, Manno EM, Lee VH, Moder KG, Keegan MT, Fulgham JR, Brown DR, Berge KH, Whalen FX, et al. Prolonged coma from refractory status epilepticus. Neurocrit Care. 2006;4(2):140–2.
Kramer U, Shorer Z, Ben-Zeev B, Lerman-Sagie T, Goldberg-Stern H, Lahat E. Severe refractory status epilepticus owing to presumed encephalitis. J Child Neurol. 2005;20(3):184–7.
Mewasingh LD, Sekhara T, Aeby A, Christiaens FJ, Dan B. Oral ketamine in paediatric non-convulsive status epilepticus. Seizure. 2003;12(7):483–9.
Haberlandt E, Weger C, Sigl SB, Rauchenzauner M, Scholl-Burgi S, Rostasy K, Karall D. Adrenocorticotropic hormone versus pulsatile dexamethasone in the treatment of infantile epilepsy syndromes. Pediatr Neurol. 2010;42(1):21–7.
Granata T, Fusco L, Gobbi G, Freri E, Ragona F, Broggi G, Mantegazza R, Giordano L, Villani F, Capovilla G, et al. Experience with immunomodulatory treatments in Rasmussen’s encephalitis. Neurology. 2003;61(12):1807–10.
Mirsattari SM, Sharpe MD, Young GB. Treatment of refractory status epilepticus with inhalational anesthetic agents isoflurane and desflurane. Arch Neurol. 2004;61(8):1254–9.
Kofke WA, Young RS, Davis P, Woelfel SK, Gray L, Johnson D, Gelb A, Meeke R, Warner DS, Pearson KS, et al. Isoflurane for refractory status epilepticus: a clinical series. Anesthesiology. 1989;71(5):653–9.
Zamponi N, Rychlicki F, Corpaci L, Cesaroni E, Trignani R. Vagus nerve stimulation (VNS) is effective in treating catastrophic 1 epilepsy in very young children. Neurosurg Rev. 2008;31(3):291–7.
Shahwan A, Bailey C, Maxiner W, Harvey AS. Vagus nerve stimulation for refractory epilepsy in children: more to VNS than seizure frequency reduction. Epilepsia. 2009;50(5):1220–8.
Abend NS, Dlugos DJ. Treatment of refractory status epilepticus: literature review and a proposed protocol. Pediatr Neurol. 2008;38(6):377–90.
Nabbout R. Efficacy of ketogenic diet in severe refractory status epilepticus initiating fever induced refractory epileptic encephalopathy in school age children (FIRES). Epilepsia (Copenhagen). 2010;51(10):2033.
Nam SH, Lee BL, Lee CG, Yu HJ, Joo EY, Lee J, Lee M. The role of ketogenic diet in the treatment of refractory status epilepticus. Epilepsia. 2011;52(11):e181–4.
Corry JJ, Dhar R, Murphy T, Diringer MN. Hypothermia for refractory status epilepticus. Neurocrit Care. 2008;9(2):189–97.
Orlowski JP, Erenberg G, Lueders H, Cruse RP. Hypothermia and barbiturate coma for refractory status epilepticus. Crit Care Med. 1984;12(4):367–72.
Kamel H, Cornes SB, Hegde M, Hall SE, Josephson SA. Electroconvulsive therapy for refractory status epilepticus: a case series. Neurocrit Care. 2010;12(2):204–10.
Rotenberg A, Muller P, Birnbaum D, Harrington M, Riviello JJ, Pascual-Leone A, Jensen FE. Seizure suppression by EEG-guided repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation in the rat. Clin Neurophysiol. 2008;119(12):2697–702.
Loddenkemper T, Cosmo G, Kotagal P, Haut J, Klaas P, Gupta A, Lachhwani DK, Bingaman W, Wyllie E. Epilepsy surgery in children with electrical status epilepticus in sleep. Neurosurgery. 2009;64(2):328–37. discussion 337.
Alexopoulos A, Lachhwani DK, Gupta A, Kotagal P, Harrison AM, Bingaman W, Wyllie E. Resective surgery to treat refractory status epilepticus in children with focal epileptogenesis. Neurology. 2005;64(3):567–70.
Ng YT, Kerrigan JF, Rekate HL. Neurosurgical treatment of status epilepticus. J Neurosurg. 2006;105(Suppl 5):378–81.
Ma X, Liporace J, O’Connor MJ, Sperling MR. Neurosurgical treatment of medically intractable status epilepticus. Epilepsy Res. 2001;46(1):33–8.
Rossetti AO, Oddo M, Liaudet L, Kaplan PW. Predictors of awakening from postanoxic status epilepticus after therapeutic hypothermia. Neurology. 2009;72(8):744–9.
Rundgren M, Westhall E, Cronberg T, Rosen I, Friberg H. Continuous amplitude-integrated electroencephalogram predicts outcome in hypothermia-treated cardiac arrest patients. Crit Care Med. 2010;38(9):1838–44.
Rossetti AO. What is the value of hypothermia in acute neurologic diseases and status epilepticus? Epilepsia. 2011;52(Suppl 8):64–6.
de Pont AC, de Jager CP, van den Bergh WM, Schultz MJ. Recovery from near drowning and postanoxic status epilepticus with controlled hypothermia. Neth J Med. 2011;69(4):196–7.
Shorvon S. Super-refractory status epilepticus: an approach to therapy in this difficult clinical situation. Epilepsia. 2011;52(Suppl 8):53–6.
Harden CL, Hopp J, Ting TY, Pennell PB, French JA, Hauser WA, Wiebe S, Gronseth GS, Thurman D, Meador KJ, et al. Practice parameter update: management issues for women with epilepsy—focus on pregnancy (an evidence-based review): obstetrical complications and change in seizure frequency. Neurology. 2009;73(2):126–32.
Jagoda A, Riggio S. Emergency department approach to managing seizures in pregnancy. Ann Emerg Med. 1991;20(1):80–5.
Karnad DR, Guntupalli KK. Neurologic disorders in pregnancy. Crit Care Med. 2005;33(10):S362–71.
Molgaard-Nielsen D. Newer-generation antiepileptic drugs and the risk of major birth defects. J Am Med Assoc. 2011;305(19):1996–2002.
Duley L, Henderson-Smart DJ, Chou D: Magnesium sulphate versus phenytoin for eclampsia. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2010(10):CD000128.
Appleton R, Choonara I, Martland T, Phillips B, Scott R, Whitehouse W. The treatment of convulsive status epilepticus in children. The status epilepticus working party, members of the status epilepticus working party. Arch Dis Child. 2000;83(5):415–9.
Singhi S, Banerjee S, Singhi P. Refractory status epilepticus in children: role of continuous diazepam infusion. J Child Neurol. 1998;13(1):23–6.
Vespa PM, Nuwer MR, Nenov V, Ronne-Engstrom E, Hovda DA, Bergsneider M, Kelly DF, Martin NA, Becker DP. Increased incidence and impact of nonconvulsive and convulsive seizures after traumatic brain injury as detected by continuous electroencephalographic monitoring. J Neurosurg. 1999;91(5):750–60.
Claassen J, Mayer SA, Kowalski RG, Emerson RG, Hirsch LJ. Detection of electrographic seizures with continuous EEG monitoring in critically ill patients. Neurology. 2004;62(10):1743–8.
Pandian JD, Cascino GD, So EL, Manno E, Fulgham JR. Digital video-electroencephalographic monitoring in the neurological-neurosurgical intensive care unit: clinical features and outcome. Arch Neurol. 2004;61(7):1090–4.
Vespa PM, O’Phelan K, Shah M, Mirabelli J, Starkman S, Kidwell C, Saver J, Nuwer MR, Frazee JG, McArthur DA, et al. Acute seizures after intracerebral hemorrhage: a factor in progressive midline shift and outcome. Neurology. 2003;60(9):1441–6.
Varelas PN, Hacein-Bey L, Hether T, Terranova B, Spanaki MV. Emergent electroencephalogram in the intensive care unit: indications and diagnostic yield. Clin EEG Neurosci. 2004;35(4):173–80.
Jordan KG. Neurophysiologic monitoring in the neuroscience intensive care unit. Neurol Clin. 1995;13(3):579–626.
Legriel S, Bruneel F, Sediri H, Hilly J, Abbosh N, Lagarrigue MH, Troche G, Guezennec P, Pico F, Bedos JP. Early EEG monitoring for detecting postanoxic status epilepticus during therapeutic hypothermia: a pilot study. Neurocrit Care. 2009;11(3):338–44.
Hirsch LJ. Continuous EEG monitoring in the intensive care unit: an overview. J Clin Neurophysiol. 2004;21(5):332–40.
Shahwan A, Bailey C, Shekerdemian L, Harvey AS. The prevalence of seizures in comatose children in the pediatric intensive care unit: a prospective video-EEG study. Epilepsia. 2010;51(7):1198–204.
Abend NS. Nonconvulsive seizures are common in critically ill children. Neurology. 2011;76(12):1071–7.
Hahn CD. Nonconvulsive seizures among critically ill children: look and you shall find. Neurology. 2011;76(12):1036–7.
Vespa PM, Miller C, McArthur D, Eliseo M, Etchepare M, Hirt D, Glenn TC, Martin N, Hovda D. Nonconvulsive electrographic seizures after traumatic brain injury result in a delayed, prolonged increase in intracranial pressure and metabolic crisis. Crit Care Med. 2007;36(7):2218–9.
Vulliemoz S, Perrig S, Pellise D, et al. Imaging compatible electrodes for continuous electroencephalogram monitoring in the intensive care unit. J Clin Neurophysiol. 2009;26(4):236–43.
Ives J. New chronic EEG electrode for critical/intensive care unit monitoring. J Clin Neurophysiol. 2005;22(2):119–23.
Vespa P. Continuous EEG monitoring for the detection of seizures in traumatic brain injury, infarction, and intracerebral hemorrhage: “to detect and to protect”. J Clin Neurophysiol. 2005;22(2):99–106.
Vespa P, Prins M, Ronne-Engstrom E, Caron M, Shalmon E, Hovda DA, Martin NA, Becker DP. Increase in extracellular glutamate caused by reduced cerebral perfusion pressure and seizures after human traumatic brain injury: a microdialysis study. J Neurosurg. 1998;89(6):971–82.
Vespa PM, McArthur D, O’Phelan K, Glenn T, Etchepare M, Kelly D, Bergsneider M, Martin NA, Hovda DA. Persistently low extracellular glucose correlates with poor outcome 6 months after human traumatic brain injury despite a lack of increased lactate: a microdialysis study. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2003;23(7):865–77.
Vespa P, McArthur DL, Glenn T, et al. Nonconvulsive seizures after traumatic brain injury are associated with hippocampal atrophy. Neurology. 2010;75(9):792–8.
Claassen J, Hirsch LJ, Mayer SA. Treatment of status epilepticus: a survey of neurologists. J Neurol Sci. 2003;211(1–2):37–41.
Goodkin HP, Yeh JL, Kapur J. Status epilepticus increases the intracellular accumulation of GABAA receptors. J Neurosc: Off J Soc Neurosci. 2005;25(23):5511–20.
Naylor DE, Liu H, Wasterlain CG. Trafficking of GABA(A) receptors, loss of inhibition, and a mechanism for pharmacoresistance in status epilepticus. J Neurosc: Off J Soc Neurosci. 2005;25(34):7724–33.
Goodkin HR, Joshi S, Kozhemyakin M, Kapur J. Impact of receptor changes on treatment of status epilepticus. Epilepsia. 2007;48(Suppl 8):14–5.
Goodkin HP, Buck ML. Still orphans: antiepileptic drug trials in children under 2 years of age. Neurology. 2008;70(22 Pt 2):2093–4.
Meldrum BS. Excitatory amino acids in epilepsy and potential novel therapies. Epilepsy Res. 1992;12(2):189–96.
Yen W, Williamson J, Bertram EH, Kapur J. A comparison of three NMDA receptor antagonists in the treatment of prolonged status epilepticus. Epilepsy Res. 2004;59(1):43–50.
Lauritzen M. Clinical relevance of cortical spreading depression in neurological disorders: migraine, malignant stroke, subarachnoid and intracranial hemorrhage, and traumatic brain injury. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2011;31(1):17–35.
Hartings JA. Spreading depolarizations have prolonged direct current shifts and are associated with poor outcome in brain trauma. Brain. 2011;134(5):1529–40.
Dohmen C. Spreading depolarizations occur in human ischemic stroke with high incidence. Ann Neurol. 2008;63(6):720–8.
Dreier JP. Delayed ischaemic neurological deficits after subarachnoid haemorrhage are associated with clusters of spreading depolarizations. Brain. 2006;129(12):3224–37.
Dreier JP, Major S, Pannek HW, Woitzik J, Scheel M, Wiesenthal D, Martus P, Winkler MK, Hartings JA, Fabricius M, et al. Spreading convulsions, spreading depolarization and epileptogenesis in human cerebral cortex. Brain. 2012;135(Pt 1):259–75.
Fabricius M. Association of seizures with cortical spreading depression and peri-infarct depolarisations in the acutely injured human brain. Clin Neurophysiol. 2008;119(9):1973.
Waziri A. Intracortical electroencephalography in acute brain injury. Annals of neurology. 2009;66(3):366–77.
Treiman DM. The role of benzodiazepines in the management of status epilepticus. Neurology. 1990;40(5 Suppl 2):32–42.
Nei M, Lee J-M, Shanker VL, Sperling MR. The EEG and prognosis in status epilepticus. Epilepsia. 1999;40(2):157–63.
Chen DK, So YT, Fisher RS. Use of serum prolactin in diagnosing epileptic seizures: report of the therapeutics and technology assessment subcommittee of the American academy of neurology. Neurology. 2005;65(5):668–75.
DeGiorgio CM, Heck CN, Rabinowicz AL, Gott PS, Smith T, Correale J. Serum neuron-specific enolase in the major subtypes of status epilepticus. Neurology. 1999;52(4):746–9.
Treiman DMGL, Marsh ST. Characterization of experimental status epilepticus by nonlinear dynamical analysis of the EEG. Epilepsia. 2005;46(Suppl 8):304.
Hirsch LJ, Brenner RP, Drislane FW, So E, Kaplan PW, Jordan KG, Herman ST, LaRoche SM, Young B, Bleck TP, et al. The ACNS subcommittee on research terminology for continuous EEG monitoring: proposed standardized terminology for rhythmic and periodic EEG patterns encountered in critically ill patients. J Clin Neurophysiol. 2005;22(2):128–35.
Acknowledgments
The committee would like to recognize and thank the following experts (listed alphabetically) who reviewed the committee’s initial recommendations and provided changes that were incorporated into the final guideline: Aaron Cook, Jeffrey Frank, Jennifer Fugate, Kathleen Hubner, Andrew Kofke, Andreas H. Kramer, Marek Mirski, Andrea Rossetti, Robert Silbergleit, and Panayiotis N. Varelas.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brophy, G.M., Bell, R., Claassen, J. et al. Guidelines for the Evaluation and Management of Status Epilepticus. Neurocrit Care 17, 3–23 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12028-012-9695-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12028-012-9695-z