Abstract
Background and aims
Cognitive and renal impairment are pervasive among elderly frails, a high-risk, geriatric sub-population with peculiar clinical characteristics. In a series of frail individuals with non-advanced chronic kidney disease (CKD), we aimed at assessing the entity of functional, general health and cognitive impairment and the possible relationship between these types of dysfunction and the severity of renal impairment.
Methods
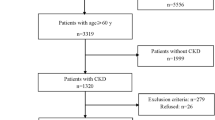
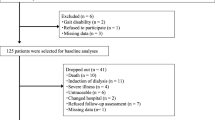
2229 geriatric subjects were screened for frailty and CKD. Severity of CKD was assessed by eGFR (CKD-EPI formula). Frailty was established by the Fried Index. Functional, general health and cognitive status were assessed by validated score measures.
Results
Final analysis included 271 frail CKD subjects (162 women, 109 men). Mean eGFR was 64.25 ± 25.04 mL/min/1.73 m2. Prevalence of mild-to-moderate CKD (stage 3–4) was 44%. Twenty-six percent of patients had severe cognitive impairment, while mild and moderate impairment was found in 7 and 67% of individuals, respectively. All subjects had poor functional and general health status. Cognitive capacities significantly decreased across CKD stages (p for trend < 0.0001). In fully adjusted multivariate analyses, cognitive status remained an independent predictor of eGFR (β = 0.465; p < 0.0001).
Conclusions
Mild-to-moderate CKD is highly pervasive among frail elderly individuals and the severity of renal dysfunction is independently correlated with that of cognitive impairment. Future studies are advocated to clarify whether the combination of kidney and mental dysfunction may portend a higher risk of worsen outcomes in this high-risk population.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bolignano D, Mattace-Raso F, Sijbrands EJ, Zoccali C (2014) The aging kidney revisited: a systematic review. Ageing Res Rev 14:65–80
Coresh J, Selvin E, Stevens LA, Manzi J, Kusek JW et al (2007) Prevalence of chronic kidney disease in the United States. JAMA 298:2038–2047
Coresh J, Astor BC, Greene T, Eknoyan G, Levey AS (2003) Prevalence of chronic kidney disease and decreased kidney function in the adult US population: Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Am J Kidney Dis 41:1–12
Fried LP, Tangen CM, Walston J, Newman AB, Hirsch C et al (2001) Frailty in older adults: evidence for a phenotype. J Gerontol A 56:M146–M156
Rockwood K, Song X, MacKnight C, Bergman H, Hogan DB et al (2005) A global clinical measure of fitness and frailty in elderly people. CMAJ 173:489–495
Dalrymple LS, Katz R, Rifkin DE, Siscovick D, Newman AB et al (2013) Kidney function and prevalent and incident frailty. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 8:2091–2099
Shlipak MG, Stehman-Breen C, Fried LF, Song X, Siscovick D et al (2004) The presence of frailty in elderly persons with chronic renal insufficiency. Am J Kidney Dis 43:861–867
Roshanravan B, Khatri M, Robinson-Cohen C, Levin G, Patel KV et al (2012) A prospective study of frailty in nephrology-referred patients with CKD. Am J Kidney Dis 60:912–921
Foster R, Walker S, Brar R, Hiebert B, Komenda P et al (2016) Cognitive impairment in advanced chronic kidney disease: the Canadian Frailty Observation and Interventions Trial. Am J Nephrol 44:473–480
Kurella Tamura M, Yaffe K, Hsu CY, Yang J, Sozio S et al (2016) Cognitive impairment and progression of CKD. Am J Kidney Dis 68:77–83
Vermeiren S, Vella-Azzopardi R, Beckwee D, Habbig AK, Scafoglieri A et al. (2016) Frailty and the prediction of negative health outcomes: a meta-analysis. J Am Med Dir Assoc 17:1163 e1161–1163 e1117
National Kidney F (2002) K/DOQI clinical practice guidelines for chronic kidney disease: evaluation, classification, and stratification. Am J Kidney Dis 39:S1-266
Farrington K, Covic A, Aucella F, Clyne N, de Vos L et al (2016) Clinical practice guideline on management of older patients with chronic kidney disease stage 3b or higher (eGFR < 45 mL/min/1.73 m2). Nephrol Dial Transplant 31:ii1–ii66
Folstein MF, Folstein SE, McHugh PR (1975) “Mini-mental state”. A practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician. J Psychiatr Res 12:189–198
Magni E, Binetti G, Bianchetti A, Rozzini R, Trabucchi M (1996) Mini-Mental State Examination: a normative study in Italian elderly population. Eur J Neurol 3:198–202
Katz S, Downs TD, Cash HR, Grotz RC (1970) Progress in development of the index of ADL. Gerontologist 10:20–30
Lawton MP, Brody EM (1969) Assessment of older people: self-maintaining and instrumental activities of daily living. Gerontologist 9:179–186
Parmelee PA, Thuras PD, Katz IR, Lawton MP (1995) Validation of the Cumulative Illness Rating Scale in a geriatric residential population. J Am Geriatr Soc 43:130–137
Esposito C, Plati A, Mazzullo T, Fasoli G, De Mauri A et al (2007) Renal function and functional reserve in healthy elderly individuals. J Nephrol 20:617–625
Coppolino G, Presta P, Saturno L, Fuiano G (2013) Acute kidney injury in patients undergoing cardiac surgery. J Nephrol 26:32–40
Leporini C, Pisano A, Russo E, D’Arrigo G, de Sarro G, et al (2016) Effect of pentoxifylline on renal outcomes in chronic kidney disease patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Pharmacol Res 107:315–332
Buemi M, Coppolino G, Bolignano D, Sturiale A, Campo S et al (2009) Arrhythmias and hemodialysis: role of potassium and new diagnostic tools. Ren Fail 31:75–80
Murphy D, McCulloch CE, Lin F, Banerjee T, Bragg-Gresham JL et al (2016) Trends in prevalence of chronic kidney disease in the United States. Ann Intern Med 165:473–481
Coppolino G, Campo S, Crasci E, Aloisi C, Giacobbe MS et al (2008) Neurobiological model and quality of life in discovering personality of the uremic patient. J Nephrol 21(Suppl 13):S139–S145
Buemi M, Caccamo C, Floccari F, Coppolino G, Tripodo D et al (2003) Correlation between quality of life assessment and a personality neurobiologic model in dialyzed patients. J Nephrol 16:895–902
Hayes TL, Larimer N, Adami A, Kaye JA (2009) Medication adherence in healthy elders: small cognitive changes make a big difference. J Aging Health 21:567–580
Buemi M, Lacquaniti A, Bolignano D, Donato V, Fazio MR et al (2008) Dialysis and the elderly: an underestimated problem. Kidney Blood Press Res 31:330–336
Bolignano D, Coppolino G, Romeo A, Lacquaniti A, Buemi M (2010) Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin levels in chronic haemodialysis patients. Nephrology 15:23–26
Berger I, Wu S, Masson P, Kelly PJ, Duthie FA et al (2016) Cognition in chronic kidney disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Med 14:206
Kurella Tamura M, Muntner P, Wadley V, Cushman M, Zakai NA et al (2011) Albuminuria, kidney function, and the incidence of cognitive impairment among adults in the United States. Am J Kidney Dis 58:756–763
Yaffe K, Ackerson L, Kurella Tamura M, Le Blanc P, Kusek JW et al (2010) Chronic kidney disease and cognitive function in older adults: findings from the chronic renal insufficiency cohort cognitive study. J Am Geriatr Soc 58:338–345
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Coppolino, G., Bolignano, D., Gareri, P. et al. Kidney function and cognitive decline in frail elderly: two faces of the same coin?. Int Urol Nephrol 50, 1505–1510 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-018-1900-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-018-1900-3