Abstract
Introduction
Osteoporotic vertebral fractures are a frequent occurrence in geriatric traumatology. Differences in the achievement of pain reduction and restoration of the height of the vertebral body after balloon kyphoplasty (BKP) or radiofrequency-targeted vertebral augmentation (RF-TVA) were to be tested on a randomized population.
Methods
A total of 80 patients (f = 59; m = 21) with osteoporotic fractures of vertebral bodies were assigned to the groups BKP (n = 44) or RF-TVA (n = 36). The clinical analyses were compared peri- and postoperatively in a prospective study with an additional follow-up examination after 1 year.
Results
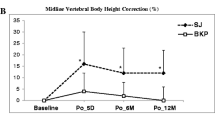
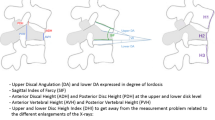
The operations for BKP were bipedicular in all cases; for RF-TVA, a bipedicular access was required in only five cases (14 %) (p > 0.0001). There were confirmed differences with respect to the amount of cement used (ml) between the two groups (BKP = 4.9 ± 1 vs. RF-TVA = 3.4 ± 1; p < 0.001). In the BKP group, the angle of kyphosis was reduced by an average of 1.65° and in the RF-TVA group by an average of 2.8° by the operation. The analysis of the maximum VAS data showed a clear postoperative reduction in the intensity of pain of approximately 4.5 cm in each of the groups with no discernible difference. After 12 months, the majority of patients in both groups (BKP = 61 % vs. RF-TVA = 83 %) reported being free of pain when at rest without a significant difference (p = 0.05).
Conclusions
A certain superiority of RF-TVA with respect to pain relief, amount of cement required, savings of operating time and personnel, and greater safety with respect to cement leakage noted in this study are consistent with other published literature. The differences between the two methods in the frequency of subsequent postoperative fractures and the secondary loss of high restoration were encouraging regarding RF-TVA.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cooper C, Atkinson EJ, O’Fallon WM, Melton LJ III (1992) Incidence of clinically diagnosed vertebral fractures: a population-based study in Rochester, Minnesota, 1985-1989. J Bone Miner Res 7:221–227. doi:10.1002/jbmr.5650070214
Pluijm S, Tromp AM (2000) Consequences of vertebral deformities. J Bone Miner Res 15:1564–1572
Schlaich C, Minne HW, Bruckner T, Wagner G, Gebest HJ, Grunze M, Ziegler R, Leidig-Bruckner G (1998) Reduced pulmonary function in patients with spinal osteoporotic fractures. Osteoporos Int 8:261–267
Silverman SL (1992) The clinical consequences of vertebral compression fracture. Bone 13(Suppl 2):S27–31
Hasserius R, Johnell O, Nilsson BE, Thorngren KG, Jonsson K, Mellstrom D, Redlund-Johnell I, Karlsson MK (2003) Hip fracture patients have more vertebral deformities than subjects in population-based studies. Bone 32:180–184
Chesnut CH, Bell NH, Clark GS, Drinkwater BL, English SC, Johnson CC Jr, Notelovitz M, Rosen C, Cain DF, Flessland KA, Mallinak NJ (1997) Hormone replacement therapy in postmenopausal women: urinary N-telopeptide of type I collagen monitors therapeutic effect and predicts response of bone mineral density. Am J Med 102:29–37
Lyles KW, Gold DT, Shipp KM, Pieper CF, Martinez S, Mulhausen PL (1993) Association of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures with impaired functional status. Am J Med 94:595–601
Wilhelm K (2003) Ballon-Kyphoplastie zur Behandlung schmerzhafter Wirbelkörperfrakturen—Technik und Ergebnisse. Fortschr Röntgenstr 175:1690–1696
Schmidt-Rohlfing B, Reilmann H, Pfeifer R, Kobbe P, Pape HC (2011) Kyphoplasty and vertebroplasty. Indications, techniques, complications and results. Der Unfallchirurg 114:431–440. doi:10.1007/s00113-011-2013-y (quiz 441–432)
Wardlaw D, Cummings S (2009) Efficacy and safety of balloon kyphoplastie compared with non-surgical care for vertebral compression fracture (FREE): a radomised trial. Lancet 373:1016–1024. doi:10.1016/s01406736(09)60010-6
Boluki D, Grifka J (2010) Vertebro- and kyphoplasty for percutaneous cement augmentation of osteoporotic vertebral body fractures. Z Rheumatol 69:454–456. doi:10.1007/s00393-010-0644-y
Gray LA, Rad AE, Gaughen JR Jr, Kaufmann TJ, Kallmes DF (2009) Efficacy of percutaneous vertebroplasty for multiple synchronous and metachronous vertebral compression fractures. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 30:318–322. doi:10.3174/ajnr.A1328
Robinson Y, Heyde CE, Forsth P, Olerud C (2011) Kyphoplasty in osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures—guidelines and technical considerations. J Orthop Surg Res 6:43. doi:10.1186/1749-799X-6-43
Rotter R, Martin H, Fuerderer S, Gabl M, Roeder C, Heini P, Mittlmeier T (2010) Vertebral body stenting: a new method for vertebral augmentation versus kyphoplasty. Eur Spine J 19:916–923. doi:10.1007/s00586-010-1341-x
Edidin AA, Ong KL, Lau E, Kurtz SM (2011) Mortality risk for operated and nonoperated vertebral fracture patients in the medicare population. J Bone Miner Res 26:1617–1626. doi:10.1002/jbmr.353
Bornemann R, Deml M, Wilhelm KE, Jansen TR, Wirtz DC, Pflugmacher R (2012) Long-term efficacy and safety of balloon kyphoplasty for treatment of osteoporotic vertebral fractures. Z Orthop Unfallchirurgie 150:381–388. doi:10.1055/s-0031-1298531
McCall T, Cole C, Dailey A (2008) Vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty: a comparative review of efficacy and adverse events. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med 1:17–23. doi:10.1007/s12178-007-9013-0
Finnern HW, Sykes DP (2003) The hospital cost of vertebral fractures in the EU: estimates using national datasets. Osteoporos Int 14:429–436. doi:10.1007/s00198-003-1395-2
Pflugmacher R, Bornemann R, Koch EM, Randau TM, Muller-Broich J, Lehmann U, Weber O, Wirtz DC, Kabir K (2012) Comparison of clinical and radiological data in the treatment of patients with osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures using radiofrequency kyphoplasty or balloon kyphoplasty. Z Orthop Unfallchirurgie 150:56–61. doi:10.1055/s-0031-1280122
Elgeti F, Gebauer B (2011) RFK for the treatment of osteoporotic and neoplastic VCF—preliminary experience and clinical results after 6 months. Mineralstoffwechsel 18:5–8
Drees P, Kafchitsas K, Mattyasovszky S, Juri S, Breijawi N (2011) Radiofrequenzkyphoplastie—Eine innovative Methode zur Behandlung von osteoporotischen Wirbelkörperkompressionsfrakturen. Mineralstoffwechsel 17 Sonderheft 1:15–19
Licht A, Kramer W (2010) Radiofrequenz-Kyphoplastie: Eine neue Methode zur Behandlung osteoporotischer Wirbelkörperkompressionsfrakturen—Eine Fallstudie. Mineralstoffwechsel 17 Sonderheft 1:35-37
Kurth A, Bayer-Helms H, Böwe C, Hartwig E, Höhne W, Jerosch J, Jöllenbeck B, Maestretti G, Vogler W, Röllinghoff M (2012) Radiofrequency Kyphoplasty—a novel vertebral augmentation system. Osteologie 3:1–6
Pflugmacher R, Bornemann R, Kabir K, Koch EMW, Randau T, Wirtz D (2011) Radiofrequenz-Kyphoplastie versus Ballonkyphoplastie in der Behandlung osteoporotischer Wirbelkörperfrakturen. Kurth AA, Orthopädische Osteologie Bremen: UNI-Med 1. Auflage: 68–72
Bornemann R, Kabir K, Otten LA, Deml M, Koch EM, Wirtz DC, Pflugmacher R (2012) Radiofrequency kyphoplasty—an innovative method for the treatment of vertebral compression fractures—comparison with conservative treatment. Z Orthop Unfallchirurgie 150:392–396. doi:10.1055/s-0031-1298547
Bornemann R, Hanna M, Kabir K, Goost H, Wirtz DC, Pflugmacher R (2012) Continuing conservative care versus crossover to radiofrequency kyphoplasty: a comparative effectiveness study on the treatment of vertebral body fractures. Eur Spine J 21:930–936. doi:10.1007/s00586-012-2148-8
Chen HL, Wong CS, Ho ST, Chang FL, Hsu CH, Wu CT (2002) A lethal pulmonary embolism during percutaneous vertebroplasty. Anesth Analg 95:1060–1062 (table of contents)
Harrington KD (2001) Major neurological complications following percutaneous vertebroplasty with polymethylmethacrylate: a case report. J Bone Joint Surg Am 83:1070–1073
Dalton BE, Kohm AC, Miller LE, Block JE, Poser RD (2012) Radiofrequency-targeted vertebral augmentation versus traditional balloon kyphoplasty: radiographic and morphologic outcomes of an ex vivo biomechanical pilot study. Clin Interv Aging 7:525–531. doi:10.2147/CIA.S37025
Liebschner MA, Rosenberg WS, Keaveny TM (2001) Effects of bone cement volume and distribution on vertebral stiffness after vertebroplasty. Spine 26:1547–1554
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
A. Petersen, E. Hartwig, and E. M. W. Koch declare that they have no conflict of interest. Mathias Wollny performs lectures and consultancy work for medical device companies inter alia DFINE, Simpirica Spine, Spinal Kinetics, Stimwave, and SI-BONE.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Petersen, A., Hartwig, E., Koch, E.M.W. et al. Clinical comparison of postoperative results of balloon kyphoplasty (BKP) versus radiofrequency-targeted vertebral augmentation (RF-TVA): a prospective clinical study. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol 26, 67–75 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00590-015-1711-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00590-015-1711-5