Abstract
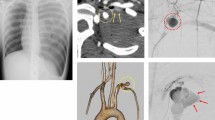
We evaluated the effectiveness of transcatheter arterial coil embolization therapy for the treatment of spontaneous hemothorax followed by aneurysm rupture in neurofibromatosis patients. Three patients were treated for massive hemothorax caused by arterial lesions associated with neurofibromatosis. Bleeding episodes were secondary to ascending cervical artery aneurysm and dissection of vertebral artery in 1 patient, and intercostal artery aneurysm with or without arteriovenous fistula in 2 patients. Patients were treated by transarterial coil embolization combined with chest drainage. In 1 patient, the ruptured ascending cervical artery aneurysm was well embolized but, shortly after the embolization, fatal hemorrhage induced by dissection of the vertebral artery occurred and the patient died. In the other 2 patients, the ruptured intercostal artery aneurysm was well embolized and they were successfully treated and discharged. Transcatheter arterial coil embolization therapy is an effective method for the treatment of spontaneous hemothorax followed by aneurysm rupture in neurofibromatosis patients.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brasfield RD, Das Gupta TK (1972) Von Recklinghausen’s disease: a clinicopathological study. Ann Surg 175:86–104
Itzchak Y, Katznelson D, Boichis H, Jonas A, Deutsch V (1974) Angiographic features of arterial lesions in neurofibromatosis. AJR Am J Roentgenol 122:643–647
Teitelbaum GP, Hurvitz RJ, Esrig BC (1998) Hemothorax in type I neurofibromatosis. Ann Thorac Surg 66:569–571
Miyazaki T, Ohta F, Daisu M, Hoshii Y (2004) Extracranial vertebral artery aneurysm ruptured into the thoracic cavity with neurofibromatosis type 1: Case report. Neurosurgery 54:1517–1520
Kipfer B, Lardinosis D, Triller J, Carrel T (2001) Embolization of a ruptured intercostal artery aneurysm in type I neurofibromatosis. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 19:721–723
Dominguez J, Sancho C, Escalante E, Morera JR, Moya JA, Bernat R (2002) Percutaneous treatment of a ruptured intercostal aneurysm presenting as massive hemothorax in a patient with type 1 neurofibromatosis. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 124:1230–1232
Niimi M, Ikeda Y, Kan S, Takami H, Furui S, Takeshita K (2002) Spontaneous rupture of an intercostal artery due to neurofibromatosis type 1 disease treated by percutaneous embolization. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 25:160–161
Deans WR, Bloch S, Leiblock L, Berman BM, Skultety FM (1982) Arteriovenous fistula in patients with neurofibromatosis. Radiology 144:103–107
Reubi F (1945) Neurofibromatose et lesions vasculaires. Schweiz Med Wochenschr 75:643–647
Salyer WR, Salyer DC (1974) The vascular lesions of neurofibromatosis. Angiology 25:510–519
Greene JF, Fitzwater JE, Burgess J (1974) Arterial lesions associated with neurofibromatosis. Am J Clin Pathol 62:481–487
Griffiths AP, White J, Dawson A (1998) Spontaneous haemothorax: A cause of sudden death in von Recklinghausen’s disease. Postgrad Med J 74:679–681
Bertram LS, Carolyn EM, Norman D, Frank R (2000) Ruptured internal carotid aneurysm resulting from neurofibromatosis: Treatment with intraluminal stent graft. J Vasc Surg 32:824–828
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arai, K., Sanada, J., Kurozumi, A. et al. Spontaneous Hemothorax in Neurofibromatosis Treated with Percutaneous Embolization. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 30, 477–479 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-006-0056-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-006-0056-1